Question
Question: For which metabolic process of plant glycolate acts as a substrate?...
For which metabolic process of plant glycolate acts as a substrate?
Solution
The smallest alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) is glycolic acid (hydroacetic acid or hydroxyacetic acid). This crystalline solid, which is colourless, odourless and hygroscopic, is highly soluble in water. In different skin-care products, it is used. In certain sugar-crops, glycolic acid is found. A glycolate, or glycolate, is a glycolic acid salt or ester.
Complete answer:
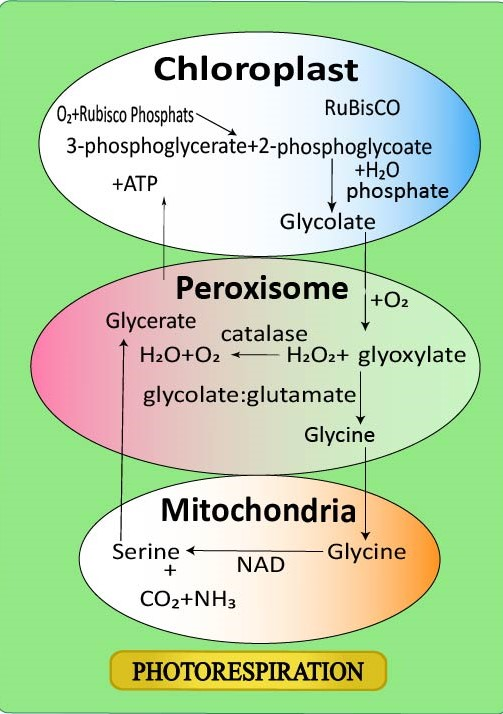
Photorespiration results in the loss of fixed carbon dioxide through the enzyme RuBisCo in C3 plants. During photorespiration, this enzyme responds to ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate with oxygen instead of carbon dioxide, producing phosphoglycolate as the first product. To produce glycolate, which is the actual substrate of photorespiration, the phosphoglycolate is dephosphorylated. Photorespiration refers to a process where the enzyme RuBisCO oxygenates RuBP in plant metabolism, wasting some of the energy provided by photosynthesis. A main step in the Calvin-Benson cycle, the desired reaction is the addition of carbon dioxide to RuBP (carboxylation), but approximately 25 percent of RuBisCO reactions instead add oxygen to RuBP (oxygenation), producing a product that can not be used throughout the Calvin-Benson cycle.This method decreases photosynthesis performance, potentially reducing photosynthetic production in C3 plants by 25 percent. Photorespiration requires a complex network of enzyme reactions that exchange metabolites between chloroplasts, mitochondria and leaf peroxisomes.
Additional information:
Indole-3-acetic acid is an acetic acid monocarboxylic acid in which a group of 1H-indol-3-yl has been substituted by one of the methyl hydrogens. It has a function as a hormone of animals, a metabolite of humans, a metabolite of plants, a metabolite of the mouse and an auxin. It is a monocarboxylic acid and an indole-3-acetic acid component.
Serine (Ser or S symbol) is an al-amino acid which is used in protein biosynthesis. It comprises an alpha-amino group, a carboxyl group (which under biological conditions is in the deprotonated-COO form), and a side chain composed of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. Under normal physiological conditions, it can be synthesised in the human body, rendering it a nonessential amino acid. The UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC codons are encoded.
So, the correct answer is ‘In Photorespiration’.
Note:
With a molecular formula of C4H6OH, malic acid is an organic compound. It is a dicarboxylic acid produced by all living organisms, which contributes to the fruit's sour taste and is used as a food additive. There are two stereoisomeric variants of malic acid, though only the L-isomer occurs naturally. Malates are referred to as the salts and esters of malic acid. In the citric acid cycle, the malate anion is an intermediate.
