Question
Question: For the principal values, evaluate \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}...
For the principal values, evaluate tan−1(−1)+cos−1(2−1).
Solution
To solve the question given above, first we will draw the rough graphs of y=tan−1(x) and y=cos−1(x) and we will determine the nature of these graphs. Then we will find the value of tan−1(−1) in terms of tan−1(1). And the values of cos−1(2−1) in terms of cos−1(21). After that, we will find the value of tan−1(−1)+cos−1(2−1) by putting the respective values.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before solving the question, we must know what is the nature of tan−1(x) and cos−1(x). For determining the nature of these inverse trigonometric functions, we will draw their respective graphs. The graph of tan−1x is:
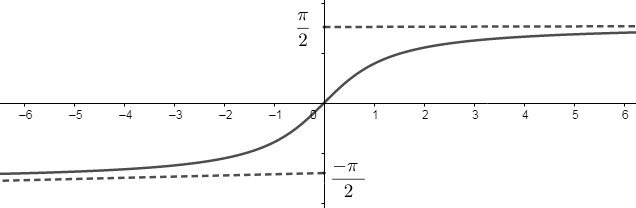
From the above graphs, we can see that the function tan−1(x) is an odd function. If a function f(x) is an odd function then we have the following relation:
So, tan−1(−x)=−tan−1(x)
Now, we will draw the graph of cos−1(x):
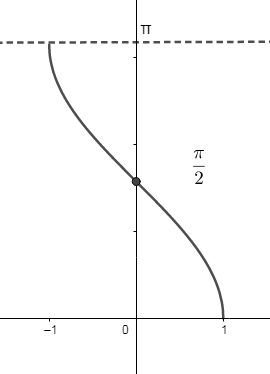
We can see from the above graph that cos−1(−x)=π−cos−1(x).
Now, we will find the value of tan−1(−1). We know that,
We have shown above that tan−1(−x)=−tan−1(x) so using this relation in solving tan−1(−1) we get,
tan−1(−1)=−tan−1(1)…………. Eq. (1)
We know that, the principal value for tan−1(1) is equal to:
4π
So, substituting this principal value in eq. (1) we get,
tan−1(−1)=−4π……… Eq. (2)
Now, we will find the value of cos−1(−21). We have shown above the following relation:
cos−1(−x)=π−cos−1(x) so using this relation in cos−1(−21) we get,
cos−1(2−1)=π−cos−1(21)……… Eq. (3)
We know that the principal value for:
cos−1(21)=4π
On putting the value of cos−1(2−1) in eq. (3), we will get:
cos−1(2−1)=π−4π
⇒cos−1(2−1)=43π ……… Eq. (4)
Now, we will add equations (2) and (4). After doing this, we will get:
