Question
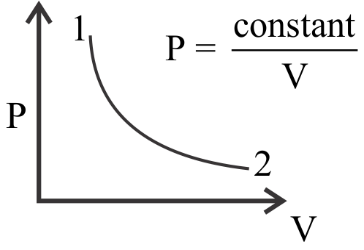
Question: . For the \(P - V\) diagram given for an ideal gas, out of the following which one correctly represe...
. For the P−V diagram given for an ideal gas, out of the following which one correctly represents the T−P diagram?
(a)

(b)
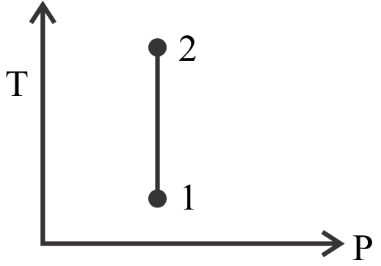
(c)

(d)

Solution
Hint We can easily solve this question by comparing the given equation with the ideal gas equation. On comparing we can determine the variance of T for the given system. So for this we will use the ideal gas equation which is given by PV=nRT . And by using this relation we can solve this question.
Formula used:
PV=nRT
This is the ideal gas equation where Pis the pressure, Vis the volume, Tis the temperature and Ris the universal gas constant.
Complete step by step answer:
The given diagram applies for an ideal gas.
Now the ideal gas equation is given as PV=RT
⇒P=VRT
It’s given in the question that P=Vconst.
Equating these two equations we can tell that in this particular system T will be constant as R is already a constant value named as the universal gas constant.
So, if we are to plot T vs P we can already tell if the value of T will remain constant. Now we see that the value of P drops from point 1 to point 2 .
In option A we see that the value of T remains fixed and the value of P at point 2 is less than its value at point 1 which is essentially what the graph in the question shows us. So this can be a correct option.
Moving further, in option B we see that value of P remains constant whereas T changes, which is not right as we know from the given question that T remains constant. So it’s not the correct option.
In option C we see that the value of P at point 2 is greater than its value at point 1 . This is opposite to what is given in the question so this is also not the correct option.
Finally in option D we see that the plotting for both the axes are wrong. The value of T changes and the value of P at point 2 is greater than its value at point 1 . So, this is also not the correct option.
Therefore the correct option is A .
Note: We should know that according to Boyle's law, when n and T is constant then the volume will have an inverse relation with the pressure which is exerted by a gas. And mathematically it can be written as v≺p1 .
