Question
Question: For the \(L - \) shaped vessel shown in the figure, determine the value of acceleration \(a\) so tha...
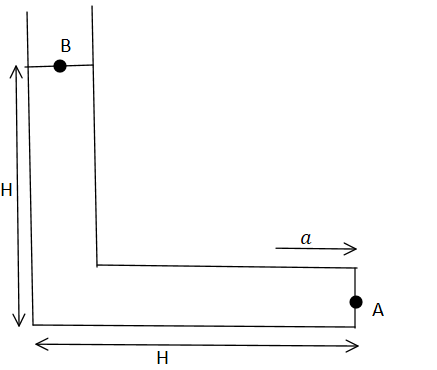
For the L− shaped vessel shown in the figure, determine the value of acceleration a so that the pressure at point A becomes equal to 2p0? (p0 is atmospheric pressure)
A) g
B) 2g+2ρHp0
C) 2ρHp0+g
D) 2ρH3p0+g
Solution
The pressure at which the atmosphere is in directly in contact with the surface is known as atmospheric pressure. Bernoulli’s theorem is based upon the conservation of total energy in a system.
Complete step by step answer:
Bernoulli’s theorem states that the total energy (pressure energy, potential energy and kinetic energy) per unit volume or mass of an incompressible and non-viscous fluid in steady flow through a pipe remains constant throughout the flow, provided there is no source or sink of the fluid along the length of the pipe.
P+ρgh+21ρv2= constant
Where, P=Pressure energy per unit volume
ρgh= Potential energy per unit volume
21ρv2= Kinetic Energy per unit volume
In the above case the total energy at Ais equal to total energy at B. So,
PA+ρaH+ρgH=PB
Where, PA= Pressure energy per unit volume at A
ρaH= Kinetic Energy per unit volume at A
ρgH= Potential energy per unit volume at A
PB= Total energy per unit volume at B
Now, given in the question that,
⇒PA=2p0
⇒PB=p0
So, 2p0+ρaH−ρgH=p0
⇒ρH(a−g)=2p0
⇒a−g=2ρHp0
Therefore, a=2ρHp0+g
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note: The atmosphere exerts the same pressure all over the earth’s surface. That pressure is known as atmospheric pressure. Its value is 1atm. Bernoulli’s theorem is another form of proof for the Law of conservation of energy.
