Question
Question: For the complex ion \[{\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 - }}\] stat...
For the complex ion [Fe(CN)6]3− state:
(i) The geometry of the ion.
(ii) The magnetic property of the ion.
Solution
Six strong field ligands are attached to the central metal atom Fe. If all the electrons in the complex ion are paired it is diamagnetic in nature. If the complex ion has an unpaired electron, it is paramagnetic in nature.
Step by step answer: Determine the geometry of the ion as follows:
In the complex ion [Fe(CN)6]3−, the ligand is CN−. The ligand CN− can accept electrons from the Fe metal atom. Thus, CN− is a strong field ligand.
As CN− is a strong field ligand. Thus, a low spin complex is formed using the inner 3d orbitals of the Fe metal atom.
There are six CN− ligands. Thus, the geometry of the complex ion [Fe(CN)6]3− is octahedral.
Determine the magnetic property of the ion as follows:
Determine the oxidation number (ON) of the central metal atom Fe as follows:
ON of Fe + 6×ON of CN−=Charge of the complex ion
Substitute (−1) for the oxidation number of CN−, −3 for the charge on the complex. Thus,
ON of Fe + 6×(−1)=−3
ON of Fe=−3+6
ON of Fe=+3
Thus, the oxidation number (ON) of the central metal atom Fe is +3.
Determine the electronic configuration as follows:
The atomic number of iron is 26. The electronic configuration of the Fe metal is 1s22s22p63s23p63d64s2.
The Fe metal is in +3 state. Thus, Fe metal loses three electrons, two from the 4s orbital and one from the 3d orbital. Thus, the electronic configuration of Fe in +3 state is 1s22s22p63s23p63d5.
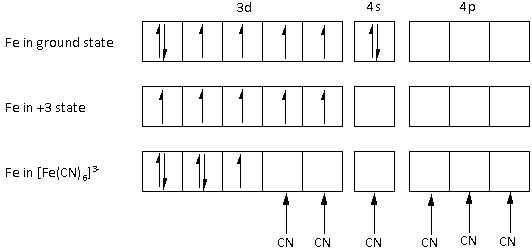
After pairing, the complex ion [Fe(CN)6]3− has one unpaired electron. Thus, the complex ion [Fe(CN)6]3− is paramagnetic.
Thus, the magnetic property of the ion [Fe(CN)6]3− is paramagnetic.
Note: The strong field ligands form low spin complexes and prefer the pairing of electrons. The weak field ligands form high spin complexes and do not prefer the pairing of electrons. The charge on the CN− ligand is −1. And the charge on the central metal atom Fe is +3 and not +2.
