Question
Question: For \[{{\text{n}}^{{\text{th}}}}\] order reaction \[\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{dx}}}}{{{\text{dt}}}}} \r...
For nth order reaction (dtdx)=Rate = k[A]0n Graph between log (rate) against log[A]0 is of the type Lines P, Q, R, S are of the order:
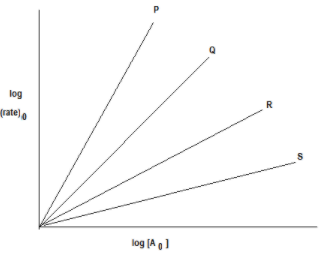
A) P-0, Q-1,R-2,S-3
B) P-3, Q-2,R-1,S-1/2
C) P-1, Q-2,R-3,S-0
D) P-0, Q-3,R-2,S-1
Solution
Take a log of both sides of the equation. Using the linear straight line equation determines the slope of the lines. By observing the effect of change in concentration on rate of reaction determines the values of order for each line P, Q, R and S.
Complete step by step answer:
For nth order reaction rate equation given to us is:
(dtdx)=Rate = k[A]0n
So, Rate = k[A]0n
Here,
n = order of reaction
k = rate constant
Now, take a log of both sides of the equation.
log(Rate ) = n log [A]0+logk
Also, we have given a graph between log (rate) against log[A]0 as follows:

From the plot log (rate) against, log[A]0we can say that all lines P, Q, R and S follow straight-line equations.
Mathematical straight line equation is:
y = mx + c
Now, comparing the straight-line equation with log(Rate ) = n log [A]0+logk equation we can say that
y =log(Rate )
x= log [A]0
m = slope = n
c = intercept =logk
Now, by observing the slope of lines we can determine the order of lines P, Q, R and S as follows:
The order of reaction is defined as the number of molecules whose concentration alters as a result of chemical change.
A reaction is said to be zero-order if the rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of the reactants. None of the lines in the graph indicates that there is no effect of change in concentration on the rate of reaction. So none of the lines are zero order.
So, options A, C and D are incorrect.
A reaction whose rate is determined by the change of one concentration term only is known as the first-order reaction. In the case of first-order reaction rate of reaction is directly proportional to the change in concentration. From the graph, we can say the order of line R is 1 as a change in concentration and change in the rate of reaction is directly proportional, that is doubling the concentration of reactant doubles the rate of reaction.
Order of line S is 1/2 as here the rate of reaction is half to that of concentration A. We can say that as the slope of the line S is 1/2 so the order of line is 1/2.
Order of line Q is 2 as the rate of reaction doubles to that of concentration A. We can say that as the slope of line Q is 2 so the order of line is 2.
Order of line P is 3 as here the rate of reaction thrice to that of concentration A. We can say that as the slope of line P is 3 so the order of line is 3.
So, the order of reaction with respect to P, Q, R and S is 3, 2, 1 and 1/2 respectively.
Thus, the correct option is (B) P-3, Q-2, R-1, S- 1/2
Note: The rate of reaction is the change in concentration of reactant or product in unit time. Change in concentration of reactants affects the rate of reaction. The mathematical relation between the rate of reaction and the concentration of the reaction component is known as the rate law expression. To determine the rate law of reaction it is necessary to calculate the order of the reaction.
