Question
Question: For all values of \( A\& B \) ,Prove that \( \cos (A - B) = \cos A.\cos B - \operatorname{Sin} A.\op...
For all values of A&B ,Prove that cos(A−B)=cosA.cosB−SinA.SinB
Solution
Hint : To calculate the value we first construct a circle and mark the points with respect to sine and cosine. Then, we will compare the two chords which subtend equal angles. Then we will be able to prove the equation by solving the equation.
Complete step by step solution:
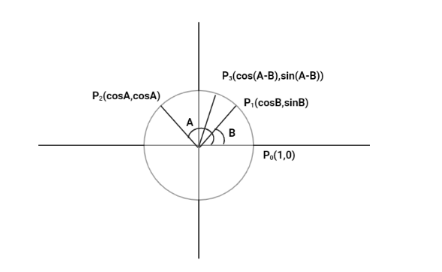
Equal chords of a circle subtends equal angle at the centre.
Hence, P1P2 chord and P0P3 chord are equal as they both angles are the same at centre that is A−B .
P0P3=P1P2 ⇒(cos(A−B)−1)2+(sin(A−B)−0)2=(cosA−cosB)2+(sinA−sinB)2
(Using the distance formula)
Now, squaring both sides we will get,
(cos(A−B)−1)2+(sin(A−B)−0)2=(cosA−cosB)2+(sinA−sinB)2 Cos2(A−B)+1−2cos(A−B)+sin2(A−B)=cos2A+cos2B−2cosAcosB+sin2A+sin2B+2sinAsinB
We know that sin2θ+cos2θ=1
Cos2(A−B)+sin2(A−B)+1−2cos(A−B)=cos2A+sin2A+cos2B+sin2B−2cosAcosB+2sinAsinB ⇒1+1−2cos(A−B)=1+1−2cosAcosB+2sinAsinB ⇒2−2cos(A−B)=2−2cosAcosB+2sinAsinB ⇒−2cos(A−B)=−2(cosAcosB−sinAsinB)
Hence, cos(A−B)=cosA.cosB−sinA.sinB
Therefore, for all values of A&B cos(A−B)=cosA.cosB−SinA.SinB
Note : Using cos(A−B) and cos(A+B) we can further derive many other formulas like cos2x, cos3x, sin2x and sin3x. All these identities can be derived in the same manner as we did in the above question.
