Question
Question: For a reaction, \(2 \mathrm { SO } _ { 2 ( \mathrm {~g} ) } + \mathrm { O } _ { 2 ( \mathrm {~g} ) }...
For a reaction, 2SO2( g)+O2( g) 2SO3( g),1.5 moles of SO2 and 1 mole of O2 are taken in a 2 L vessel. At equilibrium the concentration of SO3 was found to be 0.35molL−1The  for the reaction would be
for the reaction would be
A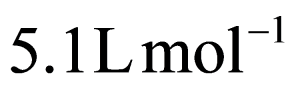
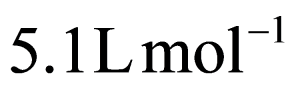
B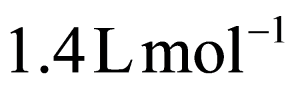
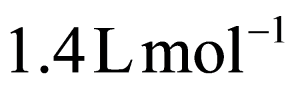
C
0.6 L mol−1
D
2.95 L mol−1
Answer
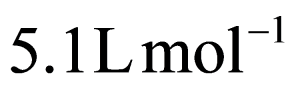
Explanation
Solution
: 2SO2( g)+  2SO3( g)
2SO3( g)
Initial conc. 21.5 21 0
At equilibrium 21.5−0.35 21−0.35 0.35
=0.4 =0.15 0.35
Kc=0.4×0.4×0.15(0.35)2=5.1 L mol−1
