Question
Question: For a given circuit, the value of current (\(I\)) is (cut in voltage for \(Si = 0.7\;{\rm{V}}\), for...
For a given circuit, the value of current (I) is (cut in voltage for Si=0.7V, for Ge=0.3V).
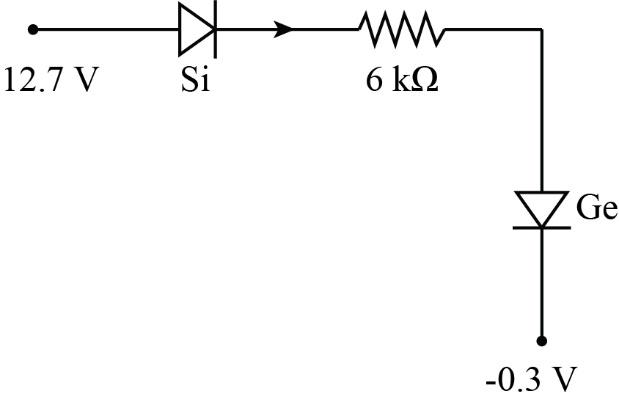
(A) 2mA
(B) 1mA
(C) 1.5mA
(D) Zero
Solution
We will identify the biasing of the diodes. Using ohm’s law, we can find the current flowing through the circuit.
A diode is formed by the combination of p type and n type semiconductors. In n type semiconductors, electrons act as supreme carriers while in p type semiconductors, holes act as supreme carriers.
Complete step by step answer:
Given,
Cut-in voltage for Si, VSi=0.7V
Cut-in voltage for Ge, VGe=0.3V
Let us find the biasing of the diodes. In the diode symbol, the arrow represents the side of the positive terminal and the vertical line represents the negative terminal of the diode.
If a positive voltage is given to the positive terminal and a negative voltage is given to the negative terminal of the diode, then the diode will be forward biased. Similarly, if we give a positive voltage to the negative terminal of the diode and vice versa, then the diode will be reverse biased.
Since +12.7V is given to the positive terminals of both the diodes and −0.3V to the negative terminals, both the diodes are forward biased.
Let VA=12.7V, VD=−0.3V and R=6kΩ
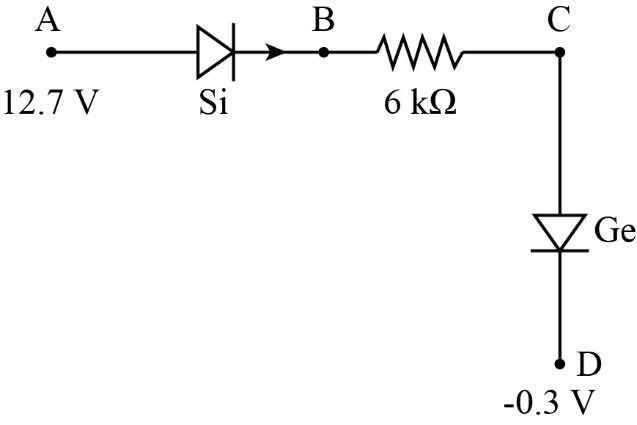
Now, the voltage at point B can be written as
VB=VA−VSi
We will substitute values of VA and VSi in the equation to get,
VB=12.7V−0.7V =12V
Now, the voltage at point C is
VC=VD+VGe
Substituting the values for VD and VGe, we get
VC=0.3V−0.3V =0V
Now the current Iflowing through the circuit is given by,
I=RVB−VC
Substituting the values of VB, VC and R, we get
I=6kΩ12V−0 =6000Ω12V =2×10−3A =2mA
So, the value of current I is 2mA.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
It is to be noted that in a diode the current flows only in one direction.
If it is forward biased, the current flows in the forward direction and if it is reverse biased, the current flows in the reverse direction.
