Question
Question: Fluorobenzene\[({C_6}{H_5}F)\] can be synthesized in the laboratory: (A) By heating phenol with \[...
Fluorobenzene(C6H5F) can be synthesized in the laboratory:
(A) By heating phenol with HF and KF
(B) From aniline by diazotization followed by heating the diazonium salt with HBF4.
(C) By direct fluorination of benzene with F2 gas
(D) By reacting bromobenzene with NaF solution
Solution
As we know that the fluorine atom is very small in size and also is an electron rich atom andF2 gas is very explosive in nature so if we use fluorine atom in direct substitution it could be very harmful in laboratory.
Complete step by step answer:
If we use fluorine gas directly it can be very explosive due to its very small size and more electrons around the fluorine nucleus.
So in laboratory we synthesis (C6H5F) indirectly, which is known as Balz-Schiemann reaction in which we will take aniline as a substrate which will react with HNO2 (nitrous acid) in the presence of fluoroboric acid and gives a product diazonium salt. As the diazo group is a good leaving group so by reacting diazo-benzene with HBF4,this fluoroboric acid attacks the diazo group and replaces diazo with fluorine atom. The HBF4 gives fluoride ion as a nucleophile which attacks on diazo group. So the final product we will get as (C6H5F).
The mechanism is shown as below.
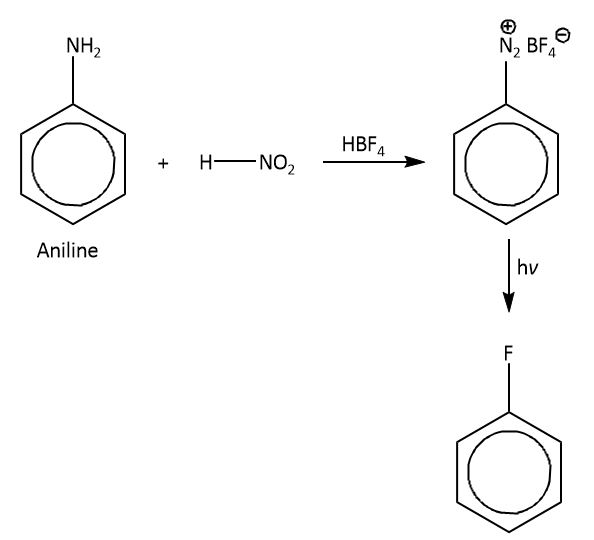
Therefore, the correct option is option (B).
Note:
Diazotization can also occur in the presence of other acids such as sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid.
