Question
Question: Find the values and then prove the expression \({{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{12}{13} \right)+{{\sin }...
Find the values and then prove the expression cos−1(1312)+sin−1(53)=sin−1(6556)
Solution
Hint: We will apply the trigonometric formula cos(θ)=HypotenuseBase and sin(a)=HypotenusePerpendicular to prove the expression. Also, we will use Pythagoras theorem here.
Complete step-by-step answer:
cos−1(1312)+sin−1(53)=sin−1(6556)
cos−1(1312)=a⇒(1312)=cos(a)
Since, we know that cos(θ)=HypotenuseBase. Therefore we can have 12 as a base and 13 as a hypotenuse of a right angled triangle as shown below. Therefore, we have
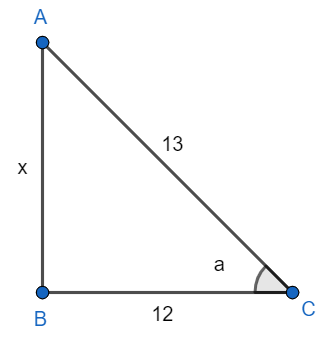
So, by Pythagoras theorem we have
(13)2=(12)2+x2⇒(13)2−(12)2=x2⇒169−144=x2⇒x2=25⇒x=5
Now this x = 5 is the value of perpendicular. Therefore, we can find the value of sin(a)=HypotenusePerpendicular. Since, perpendicular is 5 units and hypotenuse is 13. Therefore, we have sin(a)=135.
Now we will consider sin−1(53)=b. By taking the inverse sine operator to the right side of the equation we have (53)=sin(b). Since, we know that sin(a)=HypotenusePerpendicular. Therefore we can have 3 as perpendicular and 5 as a hypotenuse of a right angled triangle as shown below. Therefore, we have
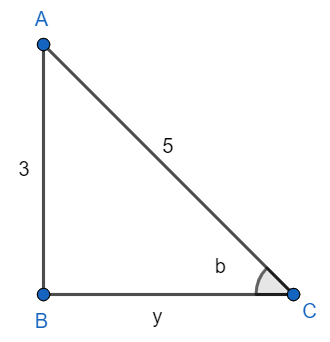
So, by Pythagoras theorem we have
(5)2=(3)2+y2⇒(5)2−(3)2=y2⇒y2=25−9⇒y2=16⇒y=±4
Since the side cannot be negative therefore we have y = 4. Now this side BC will work as a base of the triangle. Thus, we can find the value of cos(b)=HypotenuseBase. Since, the base is now 4 units and the hypotenuse is 5 units therefore we get cos(b)=54.
Now we will apply the formula sin(a+b)=sin(a)cos(b)+cos(a)sin(b). Now by substituting the values in this formula we have
sin(a+b)=135×54+1312×53⇒sin(a+b)=6520+6536⇒sin(a+b)=6556
Now we will take the sine operation to the right side of the equation. Therefore, we get sin(a+b)=6556⇒a+b=sin−1(6556)
As we know that the values of a and b are given as cos−1(1312)=a and sin−1(53)=b. Therefore, by substituting the values in the expression a+b=sin−1(6556). Therefore we get cos−1(1312)+sin−1(53)=sin−1(6556).
Hence, the expression cos−1(1312)+sin−1(53)=sin−1(6556) is proved.
Note: We could have solved it by an alternate method. In this method we can solve it as cos−1(1312)=a⇒(1312)=cos(a)
By using the trigonometry identity here which is given by cos2(a)+sin2(a)=1. This results in sin2(a)=1−cos2(a). Therefore we have
sin2(a)=1−cos2(a)⇒sin2(a)=1−(1312)2⇒sin2(a)=1−169144⇒sin2(a)=169169−144⇒sin2(a)=16925⇒sin(a)=135
Similarly, we can solve the remaining by this formula and get the desired proof.
