Question
Question: Find the value(s) of x for which \( y = {\left[ {x\left( {x - 2} \right)} \right]^2} \) is an...
Find the value(s) of x for which
y=[x(x−2)]2
is an increasing function.
Solution
Hint : To find the points or intervals where the given function is increasing, we need to follow the procedure:
Calculate dxdy , equate it equal to zero to get the values of a.
The intervals where dxdy>0 , at these the function is increasing.
Apply:
dxd(uv)=udxdv+vdxdu
Complete step-by-step answer :
We have,
y=[x(x−2)]2
Differentiating to the sides w.r.t x, we get
dxdy=2[x(x−2)]dxd[x(x−2)]
[Because dxd(xn)=nxn−1dxd(x)]
=2(x2−2x).(2x−2)
[Simplifying]
dxdy=4x(x−1)(x−2) ------(1)
Equating this to zero, we obtain:
dxdy=0
4x(x−1)(x−2)=0
The values of x are:
X=0, x=1 and x=2
Intervals can be written as:
(−∞,0),(0,1)(1,2),(2,∞)
Checking the points on the number line by substituting these in (1), we get:
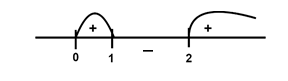
dxdy for intervals the value of x is:
(0,1) is positive
(1,2) is negative
(2,∞ is positive
Therefore, it can be said that the given function is increasing in the intervals
x∈(0,1)∪(2,∞)
Note : Always check on number line the substituted values of x in dxdy so as to confirm the interval where function increases/decreases
