Question
Question: Find the value of other five trigonometric ratios: \(\tan x = - \dfrac{5}{{12}}\) , x lies in the ...
Find the value of other five trigonometric ratios:
tanx=−125 , x lies in the second quadrant.
Solution
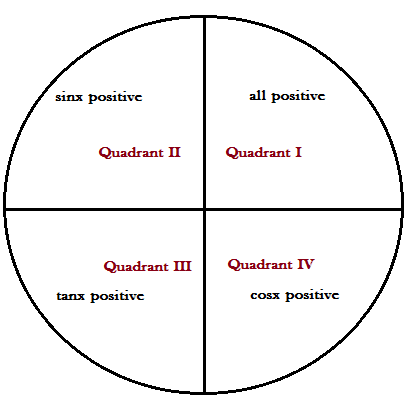
Given that x lies in the second quadrant. Now if x lies in the 2nd quadrant, only sinx and cosecx is positive.
Also, note the following important formulae:
cosx=secx1 , sinx=cosecx1 , tanx=cotx1
sin2x+cos2x=1
sec2x−tan2x=1
cosec2x−cot2x=1
Now, the value of tanx is given. Therefore find the value of the other five trigonometric ratios with the help of aforementioned formulae.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, tanx=−125
Therefore cotx=tanx1=−512
∵sec2x−tan2x=1
⇒sec2x=1+tan2x
Taking square root on both the sides we get,
⇒secx=±1+tan2x
On substituting the value of tanx we get,
⇒secx=±1+(−125)2=±1+14425
As, x lies in the second quadrant, so the value of secx is negative,
⇒secx=−1213
Therefore cosx=secx1=−1312
Now,
tanx=cosxsinx=−125
⇒sinx=cosx×(−125)
On substituting the value of cosx we get,
⇒sinx=(−1312)×(−125)=135
Therefore, cosecx=sinx1=513
Hence when tanx=−125 and x lies in second quadrant, the other five trigonometric ratios are :
cotx=−512 , sinx=135 , cosx=−1312, secx=−1213 and cosecx=513
Note: Note the following important formulae:
1.cosx=secx1 , sinx=cosecx1 , tanx=cotx1
2.sin2x+cos2x=1
3.sec2x−tan2x=1
4.cosec2x−cot2x=1
5.sin(−x)=−sinx
6.cos(−x)=cosx
7.tan(−x)=−tanx
8.sin(2nπ±x)=sinx , period 2π or 360∘
9.cos(2nπ±x)=cosx , period 2π or 360∘
10.tan(nπ±x)=tanx , period π or 180∘
Sign convention: