Question
Question: Find the total resistance across AB. Given R=\(160\sqrt 3 \Omega \). 
Solution
1. This is the recurring circuit where resistance keeps on increasing from the two ends.
2. In series connection the current flows through one resistance then through other resistance hence the total resistance is the sum of both.
3. In a parallel connection, an equivalent Connection is given by Req1=R1+R21.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we need to find the equivalent resistance across A and B
Here we can see that the resistance circuit is symmetrical to AB
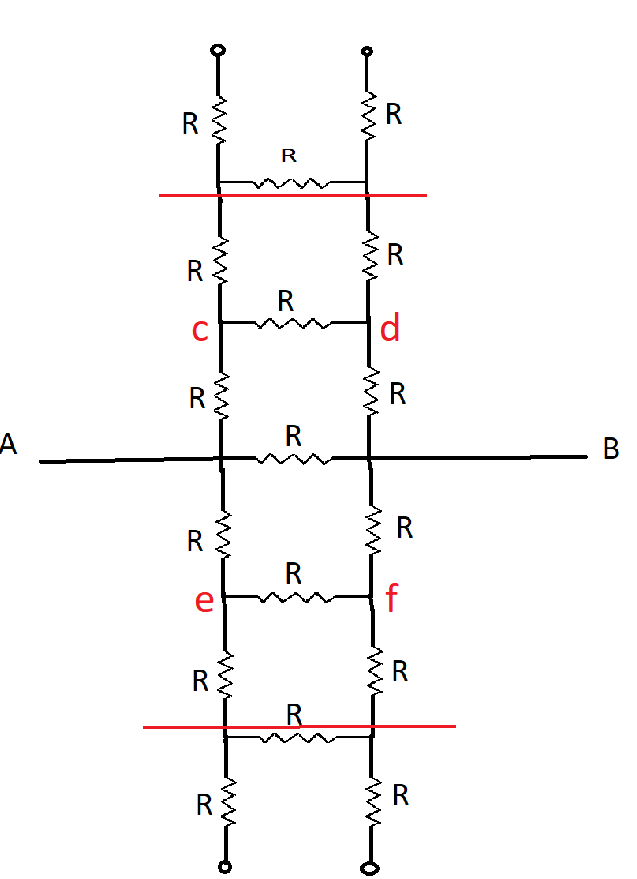
Here we can see that the circuit is infinite and repeats itself above (cd)and below (ef)
The top three resistance marked above the red line are taken as Req the same case is at the bottom also and their values will also be the same, so we substitute Reqin place of them. So now our image looks like
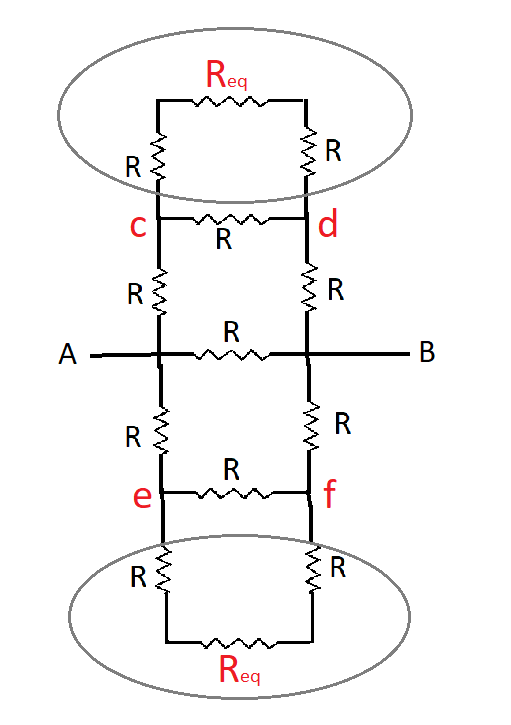
The resistance in top and bottom circles shows series connections so their equivalent resistance is given by
Req‘=Req+R+R ∴Req‘=Req+2R
Now our equivalent diagram looks like
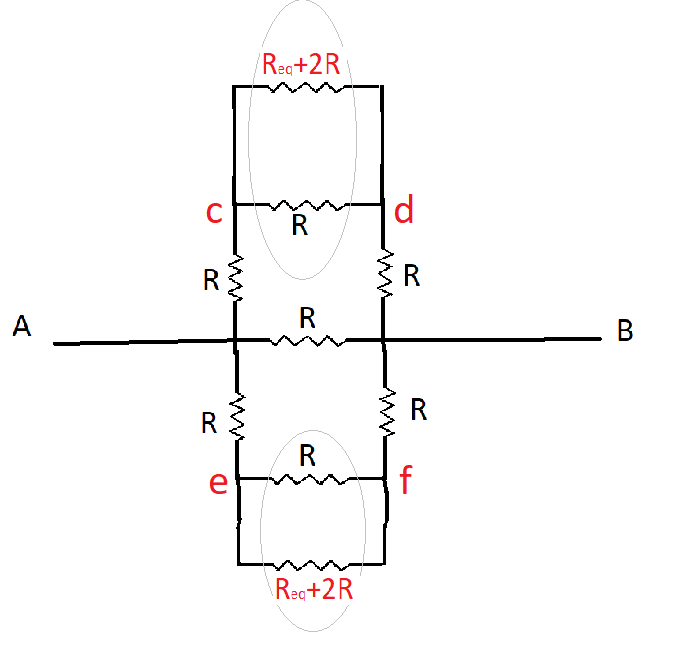
The resistance inside the circle are in parallel so there equivalent will be
Req=Req+2R+R(Req+2R)R ⇒Req=Req+3R(R×Req+2R2) ⇒Req2+3R(Req)=Req×R+2R2 ⇒Req2+2RReq−2R2=0 ⇒Req2−2R2+2RReq=0Solving the above quadratic equation we get
Req=2−2R±4R2−8R2 ⇒Req=−R+3R ⇒Req=(3−1)RNow our equivalent circuit looks like
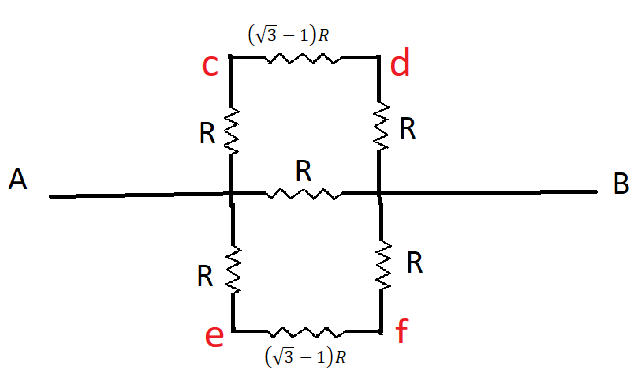
Now we see all the resistance above AB are in series so
The total resistance on each side will be
Now finally our circuit diagram looks like
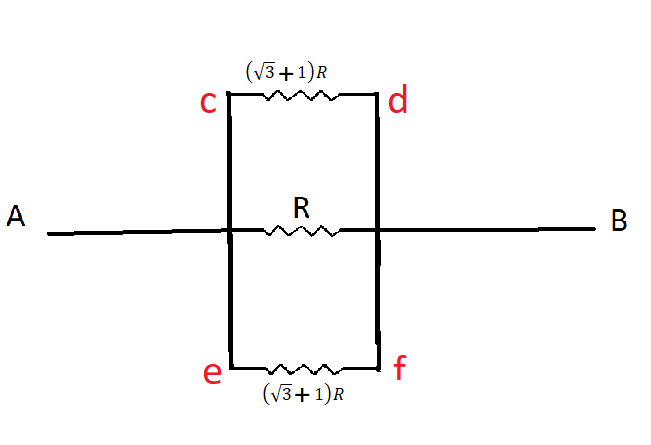
Here we can see that resistance on either side of AB are equal and parallel
AS we know two equivalent resistance of two equal resistance in parallel is half of the resistance of any one side so
Req=2(3+1)R
So final resistance will be
Here we are given that R=1603Ω
Substituting this value we get
Req=31603 ∴Req=160Ω
Final answer is, The equivalent resistance of the above circuit will be 160Ω.
Note: In these questions the assumption for Req the repeating resistance which was initially present at top and bottom is necessary.
In Series connection, the current is not divided but in parallel connection, it is divided
In a series connection, if one resistance fails then the circuit will be broken which is not in the case of parallel connection as the current will keep flowing from the other branch.
