Question
Question: Find the number of solutions of the equation tanx +secx = 2cosx in the interval \(\left[ 0,2\pi \rig...
Find the number of solutions of the equation tanx +secx = 2cosx in the interval [0,2π]
Solution
Hint: Convert tanx and secx into sines and cosines using tanx=cosxsinx and secx=cosx1. Use cos2x=1−sin2x and a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b) to factorise the expression. Using zero product property form two trigonometric equations. Find the solutions of those equations in [0,2π] and hence find the total number of solutions of the original equation in [0,2π].
Complete Step-by-step answer:
We have LHS =tanx+secx
We know that tanx=cosxsinx and secx=cosx1.
Using the above formulae, we get
LHS = cosxsinx+cosx1
Hence the equation becomes
cosxsinx+cosx1=2cosx
Taking cosx LCM on LHS, we get
cosxsinx+1=2cosx
Multiplying both sides by cosx, we get
sinx+1=2cos2x
We know that cos2x=1−sin2x
Hence we have
sinx+1=2(1−sin2x)
We know that a2−b2=(a−b)(a+b)
Hence, we have
1−sin2x=(1+sinx)(1−sinx)
Hence we have
1+sinx=2(1−sinx)(1+sinx)
Transposing terms on RHS to LHS, we get
1+sinx−2(1−sinx)(1+sinx)=0
Taking 1+sinx common, we get
(1+sinx)(1−2(1−sinx))=0⇒(1+sinx)(2sinx−1)=0
We know that if ab = 0, then a = 0 or b = 0 (Zero product property)
Hence we have
1+sinx=0 or 2sinx−1=0
Solving 1+sinx = 0:
Subtracting 1 from both sides, we get
sinx =-1
We know that sin(23π)=−1
Hence, we have
sinx=sin(23π)
We know that the general solution of the equation sinx=siny is given by x=nπ+(−1)ny
Hence we have x=nπ+(−1)n23π
Hence if x∈[0,2π], we have x=23π
Solving 2sinx-1=0:
Adding 1 on both sides, we get
2sinx=1
Dividing by 2 on both sides, we get
sinx=21
We know that sin(6π)=21
Hence we have
sinx=sin(6π)
Now we know that the general solution of the equation sinx=siny is given by x=nπ+(−1)ny,n∈Z
Hence we have
x=nπ+(−1)n6π
Taking n = 0, 1 we get
x=6π,65π
Note that when x=23π cosx = 0 and hence tanx and secx do not exist.
Hence the only solutions are x=6π,65π.
Hence the number of solutions of the equation tanx+secx=2cosx in the interval [0,2π] is two.
Note: [1] Do not forget to check whether each of the roots is in the domain or not. Failure to do so often leads to incorrect results in solving trigonometric equations.
Hence it is very important to check each of the roots in the original equation.
[2] The graph of tanx +secx (green) and 2cosx (blue) are plotted below:
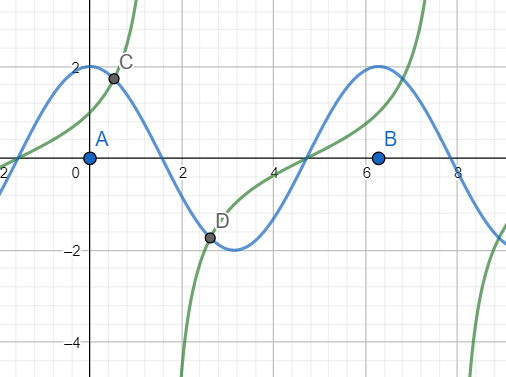
As is evident from the graph in the interval[A=0,B=2π], only two solutions exist: C and D.
