Question
Question: Find the isoelectric point pI of Lysine: (A) 5.56 (B) 9.74 (C) 6.25 (D) 0...
Find the isoelectric point pI of Lysine:
(A) 5.56
(B) 9.74
(C) 6.25
(D) 0
Solution
Hint: (1) By isoelectric point we mean the characteristic pH at which net electric charge of a molecule such as amino acid is zero.
(2) At the isoelectric point, the zwitterions form of the amino acid is dominant.
Complete step-by-step answer: If an amino acid has only one amino acid and only one carboxyl group, then the isoelectric point pI is calculated from the mean of the pKas of the amino acid molecule.
pI=2pKa1+pKa2
At a pH lower than their pI, the molecule will carry a net positive charge and at a pH higher than their pI, the molecule will carry a net negative charge. At pH equal to pI charge will be zero.
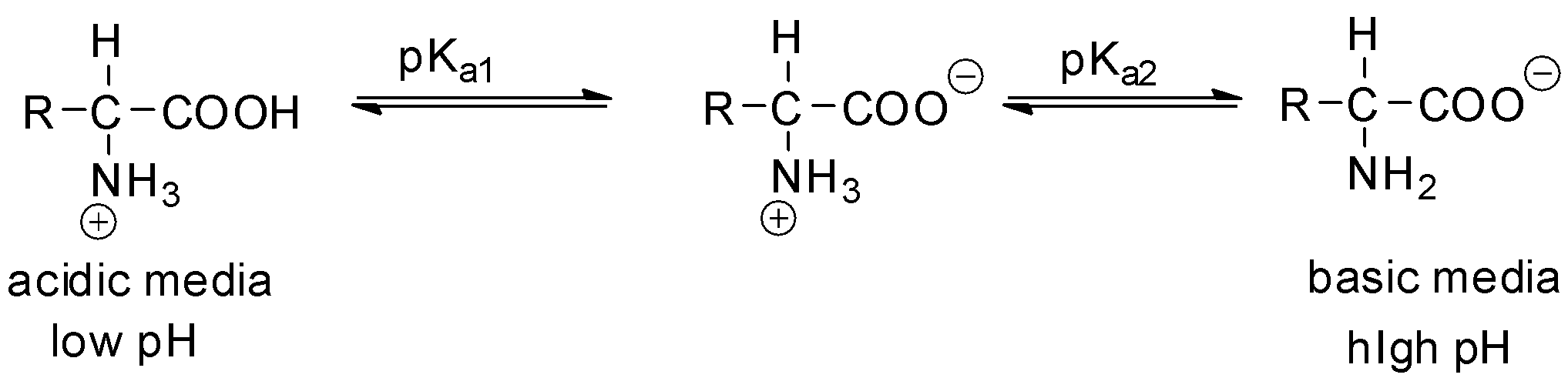
pKa1 and pKa2 are the pKas of the carboxylic acid and the amine respectively.
For amino acids having acidic and basic side chains, a third acid dissociation constant pKa3 is used to describe the ionisable groups in the side chain R.
Lysine is a basic amino acid. It is represented by the symbol Lys or K. Its structure is shown below:
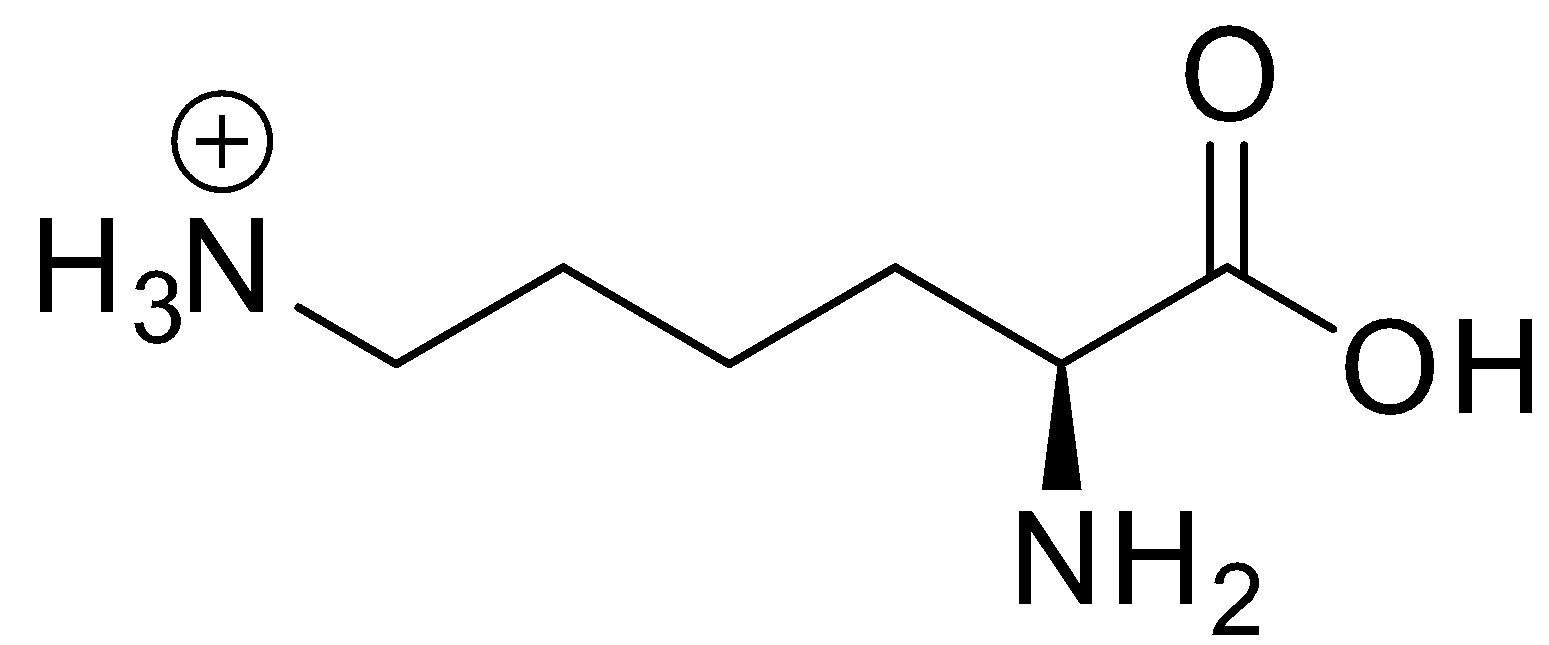
Therefore, for lysine, we can write:
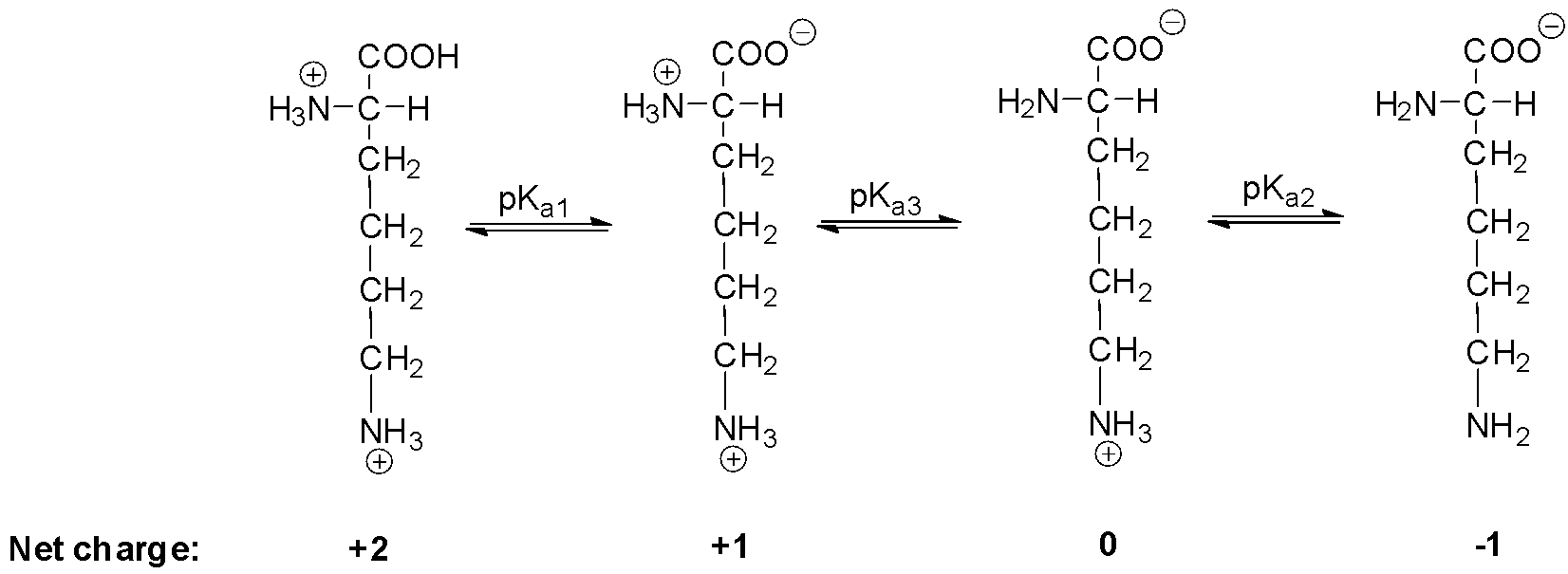
Since the isoelectric point is given by the average of the pKa values that involve the zwitterion, so we can write the formula for lysine as:
pI=2pKa3+pKa2
Now, for lysine, the pKa1 is equal to 2.18, pKa2 is equal to 8.95 and pKa3 is equal to 10.53.
Therefore, by replacing the equation by these values we will get, the isoelectric point for lysine is:
$$$$ pI=210.53+8.95=9.74
So, the correct option is (B).
Note: The isoelectric point is given by the average of the pKa values that involve the zwitterions, not just by the pKa values that describe the carboxylic acid group and the amine group. For neutral amino acids, the side chains are neutral and the isoelectric point is given simply by the average of the pKa values of carboxylic acid and amine. For acidic amino acids, the isoelectric point will be at lower pH as the acidic side chain will introduce an extra negative charge and for basic amino acids, the isoelectric point will be at higher pH as the basic side chain will introduce an extra positive charge.
