Question
Question: Find the focal length of a meniscus lens which is made of a material of refractive index \({\mu _2}\...
Find the focal length of a meniscus lens which is made of a material of refractive index μ2 for μ1<μ2<μ3 when light is incident on it. The radius of curvature of both surfaces is R. It has two different media of refractive indices μ1 and μ3 respectively on its two sides.
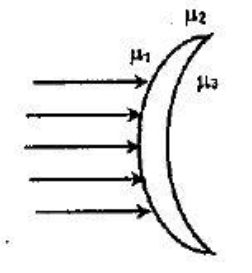
Solution
- Hint:- Use the lens maker’s formula,
vμ2−uμ1=Rμ2−μ1
where, u is the distance of object,
v is the distance of image and
R is the radius of curvature
Now, find the object distance for the first surface using this lens maker’s formula.
Next, find the image distance for the second surface using the lens maker’s formula.
Complete Step by Step Solution: -
We will use the Lens Maker’s Formula which is –
vμ2−uμ1=Rμ2−μ1
Let the refractive index of first surface and second surface be μ1 and μ2 respectively
Therefore, for first surface –
The distance of the object is at u and image distance is at infinite.
uμ2−∞μ1=Rμ2−μ1
uμ2=Rμ2−μ1
Finding the object distance u
Therefore, by transposition and cross – multiplication, we get –
u=μ2−μ1μ2R⋯(1)
This will act as an object for second refraction.
Therefore, for second surface
u=v2
Now, in lens maker’s formula, we get
vμ3−v2μ2=Rμ3−μ2⋯(2)
Because, u=v2
So, putting the value of u from equation (1) in equation (2)
vμ3−μ2Rμ2(μ2−μ1)=Rμ3−μ2 ∴vμ3−R1(μ2−μ1)=Rμ3−μ2 vμ3=Rμ3−μ2+μ2−μ1 vμ3=Rμ3−μ1
Now, finding the expression for v
v=μ3−μ1μ3R
So, the focal length for μ1<μ2<μ3 is –
Let the focal length be f
∴f=v=μ3−μ1μ3R
So, the focal length for this meniscus length is μ3−μ1μ3R.
Note:- The lens which has two spherical curved surfaces is called Meniscus lens. It is convex on one side and concave on the other side. The lens provides a smaller beam diameter in order to reduce the beam waste and spherical aberration.
