Question
Question: Find the equation of the curve in Cartesian form \[x=-1+2\sin \theta ,y=1+2\cos \theta .\] Then find...
Find the equation of the curve in Cartesian form x=−1+2sinθ,y=1+2cosθ. Then find the centre and radius of the circle.
Solution
To solve this question, we will calculate x + 1 and y – 1 then calculate the square of them using the formula (a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2 and (a−b)2=a2−2ab+b2. Finally, we will add them to get an equation of the form ax2+by2+2hxy+2gx+2fy+c=0 then the centre (a−g,a−f) and radius is a1g2+f2−ac.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given
x=−1+2sinθ.....(i)
y=1+2cosθ.....(ii)
Consider equation (i), first, we have,
x=−1+2sinθ
⇒x+1=2sinθ
Squaring both the sides of the above equation, we get,
⇒(x+1)2=(2sinθ)2
⇒(x+1)2=4sin2θ
Using the identity of the square of two numbers given as
(a+b)2=a2+2ab+b2
Using this in (x+1)2 we have
(x+1)2=x2+2x+1
⇒(x+1)2=4sin2θ
⇒x2+2x+1=4sin2θ.....(iii)
Consider the equation (ii) now, we have,
y=1+2cosθ
⇒y−1=2cosθ
Squaring both the sides of the above equation, we have,
⇒(y−1)2=(2cosθ)2
⇒(y−1)2=4cos2θ
Now, we have an identity of the square of the difference of two numbers which is given by (a−b)2=a2−2ab+b2. Using this identity in (y−1)2, we have,
(y−1)2=y2−2y+1
⇒(y−1)2=4cos2θ
⇒y2−2y+1=4cos2θ.....(iv)
To get the required equation of the curve, let us add the equation (iii) and equation (iv).
Equation (iii) is x2+2x+1=4sin2θ.
Equation (iv) is y2−2y+1=4cos2θ.
Adding these, we get,
x2+2x+1+y2−2y+1=4sin2θ+4cos2θ
⇒x2+2x+y2−2y+2=4sin2θ+4cos2θ
Using sin2θ+cos2θ=1, we get,
⇒x2+2x+y2−2y+2=4(sin2θ+cos2θ)
⇒x2+2x+y2−2y+2=4×1
⇒x2+2x+y2−2y+2=4
This is the required equation of the curve when x=−1+2sinθ and y=1+2cosθ. This is a 2-degree equation, we have,
x2+y2+2x−2y+2−4=0
⇒x2+y2+2x−2y−2=0
Finally, we have to find the centre and radius of the circle from the obtained curve.
x2+y2+2x−2y−2=0.....(v)
The general equation of the second degree is given by
ax2+2hxy+by2+2gx+2fy+c=0......(vi)
Here, the centre of the circle is given by (a−g,a−f) and the radius is given by a1g2+f2−ac.
So, finally, we will use this to get our result. Let us compare equations (v) and (vi).
⇒a=1;2=2g
⇒b=1;2f=−2
⇒2h=0;c=−2
⇒a=b=1,h=0,g=1,f=−1,c=−2
Then the centre of the circle is given by (a−g,a−f)=(−1,1). And the radius of our curve circle is given by
a1g2+f2−ac=11(1)2+(−1)2+2
⇒a1g2+f2−ac=4
⇒a1g2+f2−ac=2
Hence, the curve is given by x2+y2+2x−2y−2=0 and the centre is given by (– 1, 1) and radius = 2.
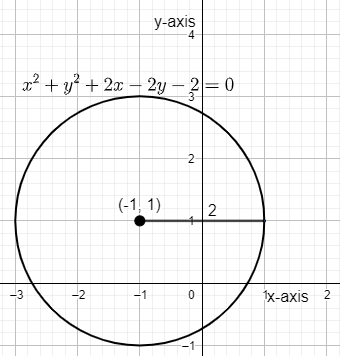
Note: Another method can be simply adding (x+1)2 and (y−1)2 and this gives (x+1)2+(y−1)2=4(sin2θ+cos2θ)=4×1=4. Then the required equation is (x+1)2+(y−1)2=(2)2. When the equation of the circle is of the form (x−a)2+(y−b)2=r2 then the centre is (a, b) and the radius = r. Comparing it from (x+1)2+(y−1)2=22 we have the centre as (– 1, 1) and the radius is 2 which is same as obtained above.
