Question
Question: Find the area between the curve \(y=\dfrac{x}{\pi }+2{{\sin }^{2}}x\), the x-axis and the ordinates ...
Find the area between the curve y=πx+2sin2x, the x-axis and the ordinates x= 0 and x=π.
Solution
Hint: Use the fact that if f(x)≥0 in the interval [a,b] then the area bounded by the curve y=f(x) and the x-axis and the ordinates x = a and x = b is given by ∫abf(x)dx. Observe that in the interval [0,π], we have πx+2sin2x≥0 and hence the area bounded by the curve y=πx+2sin2x, the x-axis and the ordinates x = 0 and x=π is given by ∫0π(πx+2sin2x)dx. Evaluate the integral and hence find the required area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
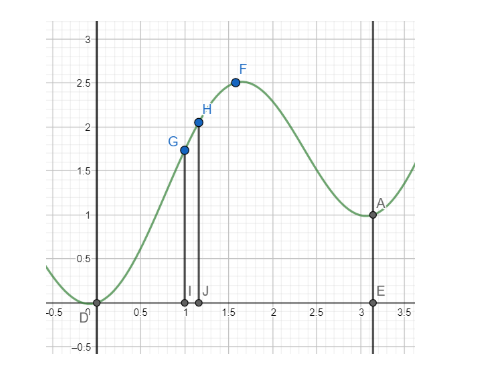
Consider the vertical strip GHJI
We have GI = y and IJ = dx
Hence the area of the strip is ydx.
The total area will be the sum of the area of the strips between D and E.
Hence, we have
Total area =∫0πydx
We know that y=πx+2sin2x
Hence, we have
Total area =∫0π(πx+2sin2x)dx
We know that ∫ab(f(x)+g(x))dx=∫abf(x)dx+∫abg(x)dx
Hence, we have
Total area =∫0ππxdx+∫0π2sin2xdx=I1+I2, where I1=∫0ππxdx and I2=∫0π2sin2x
Finding the value of I1:
We have I1=∫0ππxdx
We know that ∫abkf(x)dx=k∫abf(x)dx
Hence, we have
I1=π1∫0πxdx
We know that ∫xndx=n+1xn+1+C
Hence, we have
I1=π1(2x20π)=π1(2π2)=2π
Hence, we have I1=2π
Finding the value of I2:
We have I2=∫0π2sin2xdx
We know that ∫abkf(x)dx=k∫abf(x)dx
Hence, we have
I2=2∫0πsin2xdx
We know that if f(x) = f(2a-x), then ∫02af(x)dx=2∫0af(x)dx
Since sin2(π−x)=sin2x, we have
∫0πsin2xdx=2∫02πsin2xdx
Hence, we have
I2=4∫02πsin2x (i)
We know that ∫abf(x)dx=∫abf(a+b−x)dx
Hence, we have
I2=4∫02πsin2(2π−x)dx=4∫02πcos2xdx (ii)
Adding equation (i) and equation (ii), we get
2I2=4∫02π(sin2x+cos2x)dx
We know that sin2x+cos2x=1
Hence, we have
2I2=4∫02π1dx=4x∣02π=4×2π=2π
Dividing both sides by 2, we get
I2=π
Hence we have
Total area =2π+π=23π
Note: [1] We can calculate I2 directly using the identity sin2x=21−cos2x
We have I2=2∫0πsin2x=2∫0π21−cos2xdx=∫0π(1−cos2x)dx
We know that ∫cos2xdx=2sin2x+C
Hence, we have
I2=x−2sin2x0π=(π−0)−(2sin2π−2sin0)=π, which is the same as obtained above.
