Question
Question: Find the angle \[\theta \] for which a light ray incident at angle \({60^0}\) on the horizontal mirr...
Find the angle θ for which a light ray incident at angle 600 on the horizontal mirror becomes vertical after two successive reflections at the shown plane mirrors. Draw a ray diagram for the event. (θ is angle between plane mirrors)
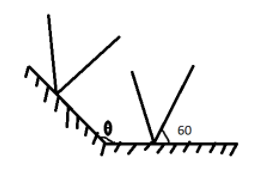
Solution
Light reflection is the basic intrinsic and essential property of the mirrors and is determined in quantitative terms by the relationship between the sum of light reflected from the surface and this effect on the surface, the term reflectivity.
Complete step by step solution:
The reflectivity of mirrors varies greatly from almost 100% for the high polished mirror of metals that reflect visible or infrasound wavelength to almost zero for highly absorbent materials. Mirrors of varying nature and structure are very diverse.
The reflections of a mirror are either actual or virtual, based on the object's proximity to the mirror, which can be correctly predicted by the geometry of a given mirror, in terms of its scale and position. Where the incident and reflected rays are crossed in front of the Spiegel, actual images are produced, while simulated images exist at points when the incident extensions and reflected rays intersect behind the Spiegel.
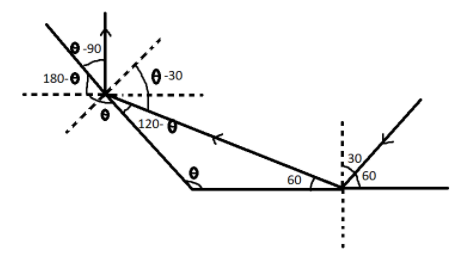
By using the mirror properties, we can write that,
1200−θ=θ−900
⇒2θ=2100
Hence, θ=1050.
Note: Optical microscopes use planar mirrors extensively for directing the beam to the optic direction, as well as for projecting pictures onto eyepieces or light sensors. The trajectory of light across paths of basic and complicated optical structures and repetitive activities like choppers, general beam deflectors and image rotators are among other applications for flat mirrors. Elliptical flat mirrors have a broad, elongated axis and are used with a minimal wave distortion for bending or plugging light at specific angles. As beam spreaders, line generators, and magnifying images along one axis, cylindrical mirrors which concentrate light on a single axis are utilised. The most famous convex mirrors in the department store, by comparison, are seen virtually everywhere, from Christmas tree ornaments to widespread security mirrors.
