Question
Question: Find potential difference between A and B 
A. 32 V
B. 98 V
C. 34 V
Solution
We need to find the total current that the connected battery drives in the circuit. For this, first determine the total equivalent resistance of the circuit. The current gets divided into two branches so the potential difference will be the product of concerned resistances and the current in the branch.
Formula used:
Equivalent resistance in series combination:
R=R1+R2 .
Equivalent resistance in parallel combination:
R1=R11R21 .
Complete step by step answer:
The given circuit has two branches, which are exactly the same. The given circuit can also be redrawn as shown below.
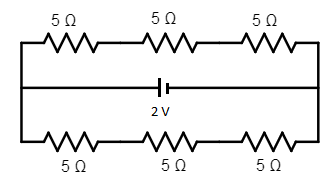
Now in any one branch, there are three 5 Ω resistances in series which gives a total of 15 Ω for one branch.
The two branches ADC and ABC are in parallel combination which will give an equivalent resistance for the entire circuit as:
R1=151+151
⟹R=15+1515×15=215Ω.
Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the entire circuit is 215Ω. The current drawn by this circuit from a battery of 2V can be written as:
I=(15/2)Ω2V=154A.
This current gets divided into two equal branches so that the current in one branch is given by:
I′=152A.
To find out the potential difference across AB, we simply multiply the resistance(s) with current. As there are two 5Ω resistances between A and B giving an equivalent of 10Ω, the potential difference is written as:
V=152×10=34V.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note:
For this question, one must remember that current gets divided when there is a parallel network involved and it remains the same for a series network. In a parallel network potential difference always remains the same.
