Question
Question: Find number of solutions of the equation \( \sin x={{x}^{2}}+x+1 \) ....
Find number of solutions of the equation sinx=x2+x+1 .
Solution
Hint : To solve the question given above, we will first find out the range of the function f(x)=x2+x+1 . To find the range, we will find out its maximum value and minimum value as infinite and for an equation ax2+bx+c=0 as −(4ab2−4ac) . Then, we will find out at what x, f(x) us minimum using x=2a−b . Then, at that value of x, we will check whether the sinx is more than the minimum value of f(x) or not. On this basis, we will determine how many solutions are there for the above equations.
Complete step-by-step answer :
To start with, we will first find out the range of the function f(x)=x2+x+1 . Now, to find the range of f(x) we will find its maximum value and minimum value. We can clearly see that the maximum value of f(x) will be infinite. Now, we know that the minimum value of the equation ax2+bx+c=0 as −(4ab2−4ac) . In our case, a = 1, b = 1 and c = 1. Thus, minimum value of f(x)=−(4(1)2−4(1)(1)) . Thus, the minimum value of f(x)=4−3 . Now, the minimum value of f(x) occurs at x=2a−b . Thus, x=2−1 . Thus, the rough graph of y=x2+x+1 is:
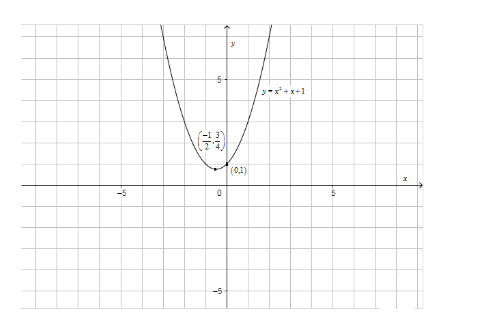
Now, we have to determine the value of sinx at x=2−1 . We know that in [2−π,0) , sinx is negative i.e. it is not possible for sinx to interest f(x) in that interval. Also, the maximum value of sinx is 1. Thus, the combined graph of y=sinx and y=x2+x+1 is shown below:
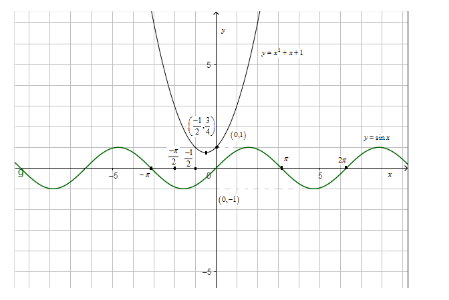
Thus, we can see that both the graphs do not intersect at all. Thus, there will be no solution of sinx=x2+x+1 .
Hence, there are 0 solutions of the equation sinx=x2+x+1 .
Note : he minima of f(x)=x2+x+1 can also be find out by an alternate method as shown below:
We know that if f(x) is a quadratic function of the form ax2+bx+c , where a>0 then its minimum value will occur at x=α where α is solution of f′(x)=0 . Thus, we have:
f(x)=x2+x+1
On differentiating both sides, we have:
⇒f′(x)=2x+1
Now, f′(x)=0 . So, we have
⇒2x+1=0⇒x=2−1
At x=2−1 , there will be minima. The value of this minima will be =f(2−1) . Thus,
f(2−1)=(2−1)2+(21)+1f(2−1)=4−3+23=43
