Question
Question: Find C and D in the given reaction. \[\underset{(A)}{\mathop{Cyclopentadiene}}\,+\underset{(B)}{\m...
Find C and D in the given reaction.
(A)Cyclopentadiene+(B)HexachlorocyclopentadieneΔ(C)Cl2/CCl4(D)
Solution
Cyclopentadiene and Hexachlorocyclopentadiene give Diels alder reaction when heated. Chlorine in presence of Carbon tetrachloride will add chlorine gas to alkene double bonds.
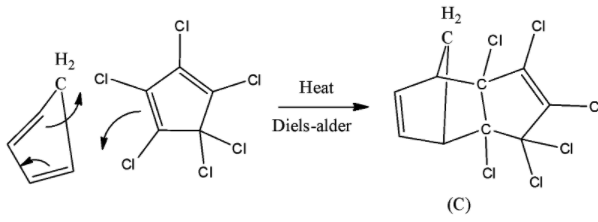
Complete answer:
Two Cyclopentadiene rings react in presence of temperature to give Diels alder reaction. Let’s see how Cyclopentadiene will react with Hexachlorocyclopentadiene in presence of high temperature.
So, both compounds will undergo Diels-alder reaction.
- Here the double bonds in Hexachlorocyclopentadiene will be less nucleophilic because of chlorine atoms in comparison with Cyclopentadiene. So, two double bonds in Cyclopentadiene will act as a diene and one double bond of Hexachorocyclopentadiene will act as a dienophile which is less nucleophilic.
Now, Chlorine in Carbon tetrachloride is a reagent that will do addition reaction on alkene and will form two new C-Cl bonds. Let’s see this reaction also.
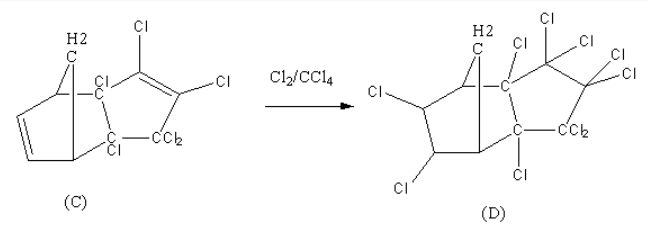
Thus we can say that (C) will be produced by Diels-alder reaction between Cyclopentadiene and Hexachlorocyclopentadiene . (D) is produced by an additional reaction where chlorine gas is added to two Carbon-Carbon double bonds.
Additional Information:
- Diels alder reaction is a kind of a (4 + 2) cycloaddition reaction. In this reaction, a conjugated diene reacts with a Dienophile and forms a cyclic structure. That’s why this reaction is called a cycloaddition reaction.
- Remember that in cycloaddition reactions, Diene donates electrons first, so it needs to be more nucleophilic than the Dienophile.
Note:
Remember that 4+4 cycloaddition reactions between Cyclopentadiene and Hexachlorocyclopentadiene do not occur. Chlorine in Carbon tetrachloride do not substitute chlorine atoms with H-atoms which are bonded to carbon.
