Question
Question: Figure shows part of a circuit. If \(I{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}7{\text{ }}A\) and is decreasing at a c...
Figure shows part of a circuit. If I = 7 A and is decreasing at a constant rate of 500 A/s, then VB − VA is
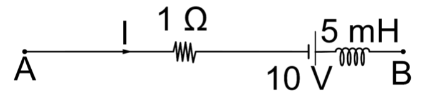
A. − 1.5 V
B. 2.5 V
C. − 3.5 V
D. 5.5 V
Solution
We will directly form an equation as we move from A to B using the conventions of Kirchhoff’s rule. Then, we will substitute the appropriate values and then evaluate the required solution.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly we start from point A and we start the equation with VA. Then, we move to the resistor and we observe that we are moving with the current in the resistor and thus we will have a potential drop thus, we proceed with VA − IR.
Now, we reach the cell and we are moving from the negative to the positive end which means we are moving from a point of lower potential to a point of higher potential and thus, we will have a potential lift.Thus, we get
VA − IR + V
Then, we reach the inductor and we move along with the current and thus there is a potential drop.Thus, we get
VA − IR + V + L dtdI
Finally, we reach the final point B. Thus, we get
VA − IR + V + L dtdI = VB
Further, we rearrange the equation and we get
VB − VA = V + L dtdI − IR −−−−−−− (i)
Now, we will observe the given values
V = 10 V
⇒R = 1 Ω
⇒I = 7 A
As an inductor opposes the flowing current.
Thus, the value of inductance will be negative.
L = − 5 mH = − 5 × 10−3 H
Since, there is a current decay in the inductor. Thus, the value of dtdI is negative.Thus,
dtdI = − 5 × 102 A/s
Substituting these values in equation (i), we get
VB − VA = 10 + (5 × 10−3) × (5 × 102) − 7 × 1
Further, we get
VB − VA = 10 + 25 × 10−1 − 7
Then, we get
VB − VA = 3 + 2.5
Finally, we get
∴VB − VA = 5.5 V
Hence, the correct answer is D.
Note: Students should be very cautious while using the values of inductance and current decay. Students should use the idea of exponents as otherwise, they will arrive into a situation of clumsy calculations.
