Question
Question: Figure shows a mixture of blue, green and red coloured rays incident normally on a right angled pris...
Figure shows a mixture of blue, green and red coloured rays incident normally on a right angled prism. The critical angles of the material of the prism for red, green and blue are 46∘,44∘and 43∘ respectively. The arrangement will separate:
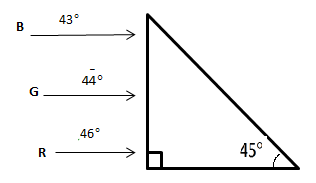
A. Red colour from blue and green
B. Blue colour from red and green
C. Green colour from red and blue
D. All the three colours.
Solution
At 45∘, all three rays will touch the prism hand, so the angle of incident is 45∘. The ray that has a higher angle than 45∘ will undergo internal reflection and will be separated from the other two rays.
Complete step by step answer:
Given,
The critical angles of the material of the prism for red, green and blue are 46∘, 44∘and 43∘ respectively.
By setting the refraction angle equal to 90∘, the critical angle can be determined from Snell's law. Part of the incident light will be emitted to any angle of incidence other than the critical angle and part would be replicated.
To scatter light into a continuum or to reflect rays of light, a translucent rigid body, often with triangular bases, is used. In geometry, a solid with parallel, congruent polygons and parallelograms with bases or ends is the prism.
Internal reflection: In optics, a beam of light through a medium, such as water or glass, is completely mirrored back into the medium from the surrounding surfaces. When the angle of incidence is greater than that limiting angle, named the critical angle, the anomaly happens.
Since, the angles of blue ray and the green ray are less than 45∘, they will transmit through the prism. But the angle of the red ray is more than 45∘. Therefore, it will undergo total reflection.
Thus, the red ray will be separated from blue and green rays.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Since red's critical angle is greater than 45∘, it is also the only colour that would not be fully mirrored, so red is segregated from green and blue.
