Question
Question: Faraday’s second law of electromagnetic induction states that: A. The magnitude of the induced emf...
Faraday’s second law of electromagnetic induction states that:
A. The magnitude of the induced emf is directly proportional to the rate of change of flux
B. The magnitude of the induced emf is inversely proportional to the rate of change of flux
C. The direction of the induced emf is such that it opposes the change in flux
D. The magnitude of the induced emf is directly proportional to the square of the rate of change of flux.
Solution
Faraday's law of induction is the basic law of electromagnetism which defines how a magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit in order to produce an electromotive force (EMF). Induction is a phenomenon in which if we run an electric current through a wire then it will produce a magnetic field around the wire.
Complete answer:
According to Faraday’s second law of electromagnetic induction, the induced voltage in a circuit is directly proportional to the rate of change over time of the magnetic flux through that circuit or we can say that the faster the magnetic field changes greater will be the voltage in the circuit and the direction of this change in the magnetic field determines the direction of the current. Mathematical expression of Faraday’s Law is ; E=−dtNdΦ where E is electromagnetic induction, N is number of turns in coil and dtdΦ is rate of change of flux.
In order to increase the voltage we increase the number of loops in the circuit, the induced voltage in a coil with two loops will be twice that with one loop and triple with three loops, that's why the real motors and generators typically have a large number of coils. We can understand how induced emf is generated by a simple experiment in which a bar magnet is moved toward a coil and emf is generated.
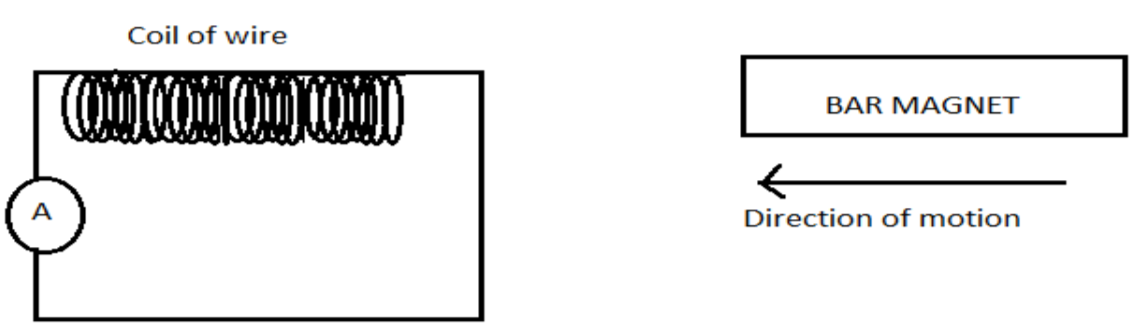
One of the important application of Faraday’s Law of Induction is the transformer in which the alternating current which changes the direction many times per second is sent through the coil which is wrapped around the magnetic core and this produces a changing magnetic field in the core resulting in induction of current in the second coil which is wrapped around a different part of the same magnetic core.
Hence the correct option is A.
Note: The ratio of the voltage between the input and output current depends upon the ratio of the number of turns in the coils for example if we take a transformer with around 100 turns on the input side and around 50 turns on the output side and we input 220 volts of alternating current then the output will be of 110 volts.
