Question
Question: \[{F_2}\] ratio of chicken came out to be 9 rose comb blacks, 1 single comb white, 3 rose comb white...
F2 ratio of chicken came out to be 9 rose comb blacks, 1 single comb white, 3 rose comb whites and 3 single comb blacks. Which are the recessives?
A. Single comb, white plumage
B. Rose comb white plumage
C. Single comb black plumage
D. Rose comb black plumage
Solution
A genetic Dihybrid cross involves crosses between organisms that differ in two traits. According to the laws of inheritance, the off-springs formed from such crosses exhibit a particular phenotype or visible trait.
Complete answer:
A genetic cross is mating between two individuals resulting in the formation of a zygote. If the cross is between two organisms that differ in a single character or trait, it is known as Monohybrid cross. If the cross involves two organisms that differ in two different traits, it is known as Dihybrid cross.
For example, if we perform a cross between two chickens who differ in their comb appearance, such as Rose comb and Single comb, the cross will be Monohybrid. However, if the cross is between two chickens, one of which has a Rose comb and is with black plumage, and the other exhibits Single comb and white plumage, it will be a hybrid cross.
These crosses were first studied by Gregor Johan Mendel on pea plants. He chose the pea plants with different characters such as height, pod colour, pod shape, etc. These studies led him to conclude that a character is influenced by a single with two alternative forms. These alternative forms are known as alleles. One allele can be dominant over the other allele. Dominant traits are expressed in the next generation while recessive traits are suppressed.
Here, two more terms are of immense importance – phenotype and genotype. Phenotype is the visible characters of an individual and genotype, the genetic make-up.
These studies led Mendel to write the Laws of Inheritance. According to these laws, if we study a cross between two individuals, for two traits (that is, a dihybrid cross) – one having two dominant trait and the other one with two recessive traits, the first generation or the F1 generation will demonstrate the dominant traits only. If the members of the F1 generation are crossed, the second generation or the F2 generation will exhibit both the dominant trait and the recessive trait in different combinations. The phenotypic ratio will be 9:3:3:1.
Here, 9 represents individuals showing both dominant traits.
3 individuals representing the first dominant trait and the second recessive trait.
3 individuals with the first recessive trait and the second dominant trait.
1 individual exhibiting both the recessive traits.
A Dihybrid cross can be better understood with the help of the following diagram:
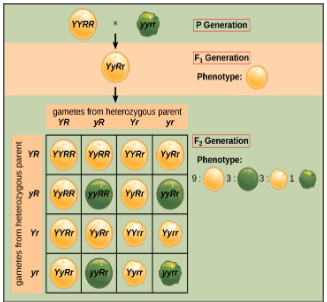
Fig: Representation of Mendel’s Dihybrid cross
According to the question, only one individual represents Single comb and white plumage. Therefore, these characters are recessive ones.
Hence, option (A) is correct.
Note: Gregor Johan Mendel, with the help of these experiments, went on to write three laws of Inheritance – the Law of Dominance, Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent assortment. These laws helped us to study patterns of inheritance. It explained why offsprings differ from their parents. It helped us understand the chromosomal theory of inheritance.
