Question
Question: Explain with example how traits get expressed?...
Explain with example how traits get expressed?
Solution
The controlled and integrated actions of genes can produce specific sets of proteins with characteristic structures that carry specific modifications needed for the cells to function.
Complete answer:
Traits are coded in the form of genes and genes are the sequences which code for particular polypeptides which lead to the formation of particular proteins. Proteins then lead to the expression of particular traits.
The gene which decides the physical appearance of an organism even in the presence of another alternative gene is known as a dominant gene. The trait expressed is called a dominant trait. A dominant trait is expressed only when two copies of the genes are present. The dominant gene is denoted by a capital letter. The gene which decides the physical appearance of an organism only in the presence of another similar gene is called a recessive gene. The trait expressed is called a recessive trait. The recessive gene is denoted by a small letter.
In an example of the pea plant, there are two types of genes for the plant height-‘T’ and ‘t’. In this, pure tall (TT) pea plant was crossed with dwarf (tt) plant.
In F1 Generation: All the plants obtained were heterozygous tall (Tt). These plants from F1 generation were self-pollinated to obtain F2 generation.
In F2 Generation: In this cross one homozygous tall plant (TT), two heterozygous tall plants (Tt) and one homozygous dwarf plant (tt) were obtained.
In F2 Generation: In this cross one homozygous tall plant (TT), two heterozygous tall plants (Tt) and one homozygous dwarf plant (tt) were obtained. 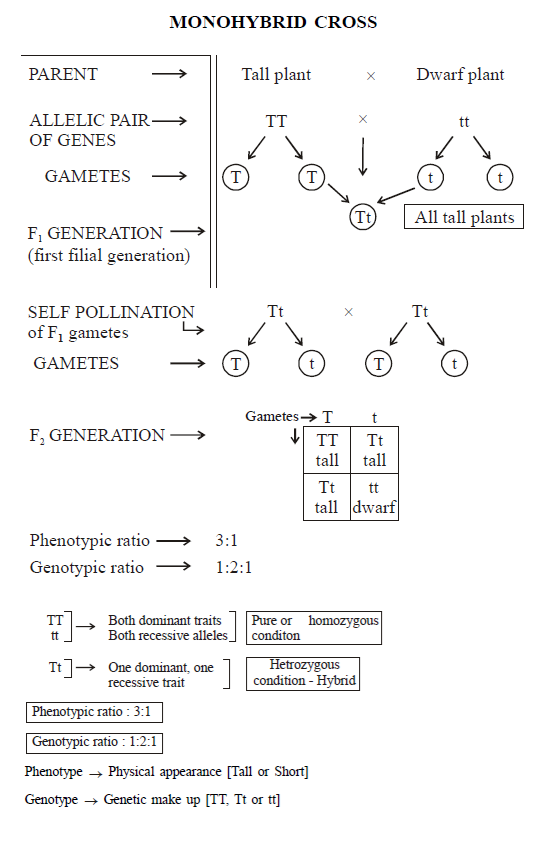
Note: In both, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, controlled and integrated actions of genes can produce specific sets of proteins with characteristic structures that carry specific modifications needed for the cells to function. This process is called “gene expression”, which refers to the conversion of the information encoded in a gene first into messenger RNA and finally to a protein.
