Question
Question: Explain what is meant by electrolysis of water. Write the electrode reactions and explain them....
Explain what is meant by electrolysis of water. Write the electrode reactions and explain them.
Solution
Electrolysis of water is the decomposition into oxygen and hydrogen gas of water. We have to do electrolysis of water and write the equations for anode and cathode. Water (H2O) will decompose in O2 and H2 gases because water (H2O) use the composition of these two gases.
Complete answer:
Electrolysis is the process by which ionic substances are decomposed (broken down) into simpler substances when an electric current is passed through them.
Electricity is the flow of electrons or ions.
It is also called water splitting.
It requires a minimum potential difference of 1.23 volts to split water.
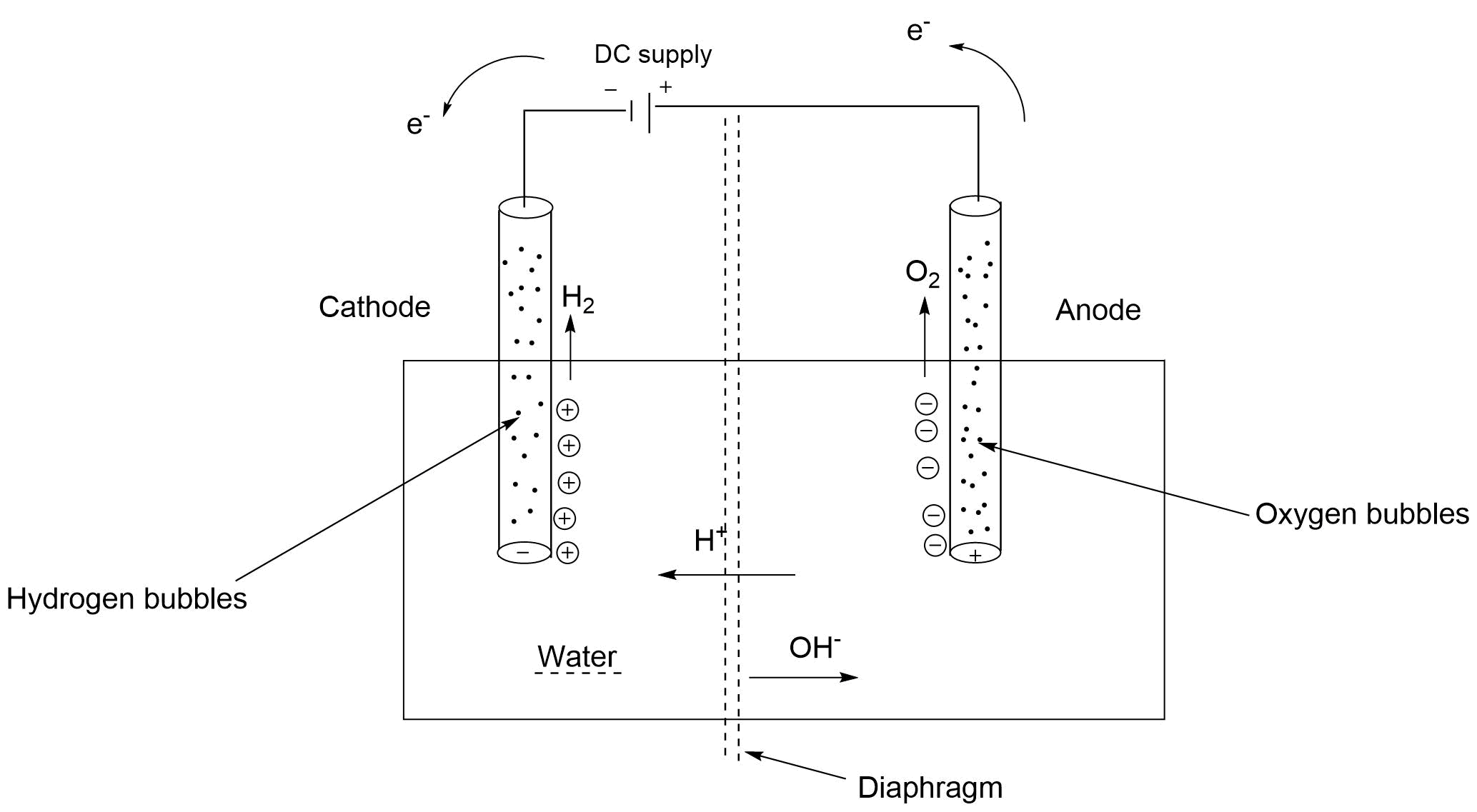
At anode:
2H2O(l)O2(g)+4H+(aq)+4e−
Or H2O(l)2H++21O2+2e−
At cathode:-
2H++2e−→H2
Net reaction:-H2O→H2+21O2
When we apply DC current in the CKT then at anode H+ ions will produce and they will attract cathode. O2 Gas will also be there.
At cathode: H2 gas will produce and OH− ions attract to anode.
We can see in the equation that the amount of O2 gas will help than H2 gas.
Volume of H2 is double than O2(g)
In the net reaction we get one mole of H2(g) and half mole of O2(g) from one mole of water.
The electrolyte and the electrodes used in electrolysis form an electrolyte, the positive ions of the electrolyte move toward the cathode (negative electrode), where they gain electrons to become a neutral substance.
Additional information: Uses of Electrolysis:
Electrolysis is commonly employed for coating one metal with another. The method of coating one metal with another using an electric current is called electroplating.
Note:
-After electrolysis of water, H2(g) is collected at negative cathode and O2(g) is collected at the positive anode.
-Hydrogen is double in volume than oxygen.
-Electrolysis water is one such most capable method for production of hydrogen because it uses renewable (H2O) and produces only pure oxygen as by product.
