Question
Question: Explain Valence Bond Theory....
Explain Valence Bond Theory.
Solution
The valence bond theory was proposed by the German physicists Walter Heinrich Heitler and Fritz Wolfgang London. It explains the formation of covalent bonds due to the physical overlap of half-filled valence atomic orbitals of two different atoms. The valence bond theory can explain the electronic structures of several molecules.
Complete answer:
Valence bond theory was proposed by German physicists Walter Heinrich Heitler and Fritz Wolfgang London. This theory explains the covalent bond formation and also the electronic structures of molecules.
So, the VBT assumes that the electrons are present in atomic orbitals of atoms in a molecule and the electrons of one atom are attracted by the nucleus of another atom.
We will now see the postulates of Valence Bond Theory:
-Covalent bonds are formed due to the overlapping of half-filled valence atomic orbitals of two different atoms. Due to this overlapping, electron density increases in the bond between two atoms and hence increases the stability of the resultant molecule.
-The atomic orbitals which have more than one unpaired electrons can form multiple bonds. Paired electrons cannot participate in bond formation.
-Covalent bonds between two atoms are directional in nature and are parallel to the region of overlapping atomic orbitals.
-Due to the overlap of atomic orbitals, two types of bonds are formed: sigma ( σ ) and pi ( π ) . Sigma bonds are formed by the overlapping of orbitals along the axis containing nuclei of two atoms whereas pi bond is formed by the sidewise overlapping of atomic orbitals.
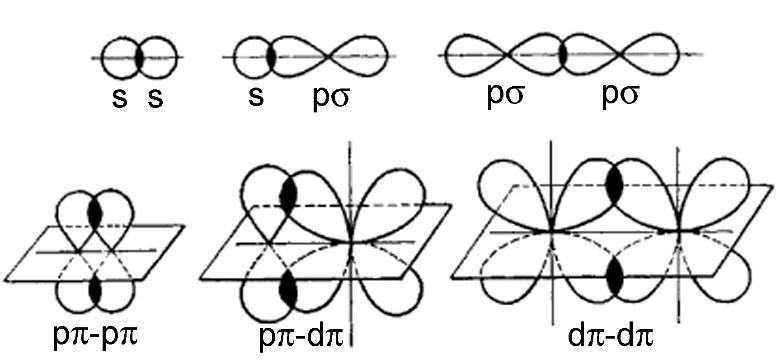
The theory assumes that electrons occupy atomic orbitals of individual atoms within a molecule, and that the electrons of one atom are attracted to the nucleus of another atom.
When the atoms are very far, there is no interaction between them. So, we can say that the total energy of the system is zero. As the atoms come closer, their orbitals start interacting. The electrons of one atom feels the attraction of the nucleus of another atom, while there is a force of repulsion between the electrons of atoms and the nuclei of two atoms.
This attraction increases as the atoms approach one another until the atoms reach a minimum distance. At this distance, the stability of the molecule is maximum and the potential energy is minimum.
If the distance between these atoms decreases further, the repulsion force will dominate over the attraction forces. The energy of the system will increase, making it destabilize.
Note:
Valence bond theory explain covalent bonding as well as structure of molecule, but it has some limitations such as, it assumes that electrons are localised which is not true, it does not explain the thermodynamic and kinetic stability of the molecules and also it does not explain the tetravalency of carbon.
