Question
Question: Explain the term structural isomerism giving example....
Explain the term structural isomerism giving example.
Explanation
Solution
Isomers are the molecules that have the same molecular formula but a different structure. The isomer which has the same molecular formula but the difference in connectivity of bond or functional group is called the structural isomers. For example, (C4H10)exist as n-butane or 2-methyl propane.
Complete step by step solution:
Isomers are defined as the molecules which have the same molecular formula but have a different arrangement of atoms in space. These include the different arrangement of atoms in space, due to the rotation of the molecule. They are classified as,
- Structural isomers
- Stereoisomers
The isomers in which the atoms are arranged in a completely different order with that of the molecular formulas. The isomers which differ in the atomic arrangement of the atoms in molecules without any kind of reference to the spatial arrangement are called the structural isomers.
This is also called as the constitutional isomerism.
These isomers have the same molecular formula but different connectivity between the atoms. For example, the alkane having the molecular formula (C4H10) can be represented in different isomers. The number of structural isomers increases with the increase in the number of carbon atoms.
Let us take an example of structural isomerism.
The molecular formula (C5H12)can be represented as follows:
CH3 \-CH2\-CH2(n-pentane)\-CH2\-CH3 !!∣!! CH3 \-CH2\-CH3 CH\-CH3 !!∣!! CH3 !!∣!! \-CH3 C CH3\-CH3 (2-methylbutane) (2,2-Dimethylpropane)
In the above structures, the molecular formula is (C5H12)but differ in the arrangement or connectivity of bonds.
There are three types of structural isomers. These areas follow: - Chain isomerism: This is a type of structural isomerism. The chain isomerism arises when there is a difference in the atomic arrangement of the carbon to carbon chain in molecules. This is observed when the compounds have the same molecular formula but the difference in the main chain. This is also called as the skeletal isomerism. For example, the (C5H12)can be arranged in three different structures, n-pentane where the main chain contains 5 carbons, iso-pentane where the main chain contains 4 carbons, and neopentane where the main chain contains the three carbon atoms.
- Position isomerism: Position isomerism arises when there is a difference in the position acquired by the substituents or unsaturated group or functional group in the chain. The position of functional group changes concerning the main chain. For example,
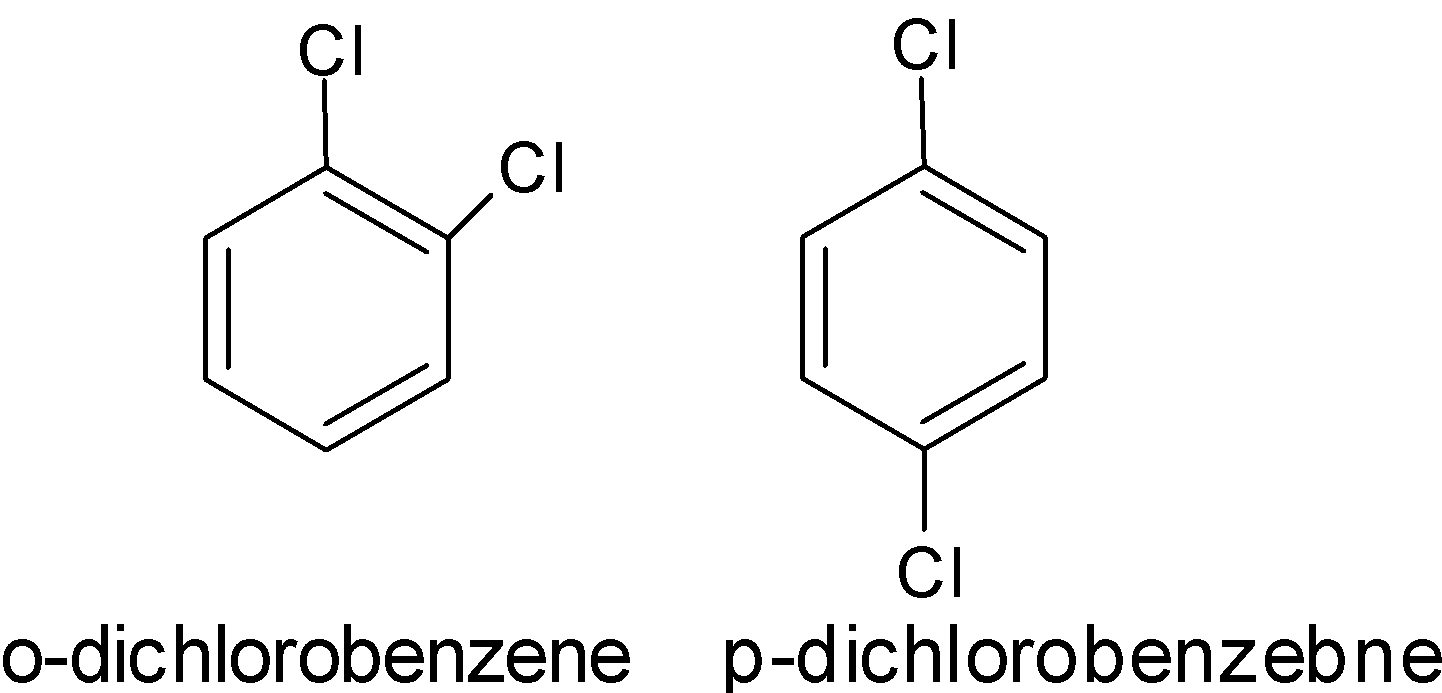
- Functional group isomerism: The functional group isomerism arises due to the presence of an odd form of functional group with the same molecular formula. The compounds have the same molecular formula but have two different structures and contain the different functional groups. For example,
