Question
Question: Explain the mechanism of opening and shutting of stomata....
Explain the mechanism of opening and shutting of stomata.
Solution
There are certain parts altogether green plants which are essential and play a critical role in several life processes. Stomata is one of the essential parts that's involved in gaseous exchange. There are thousands of stomata on the surface of the leaves. Most of those are found on the lower side of the leaves.
Complete answer:
Stomata are the small openings present on the epidermis of leaves. we will see stomata under the sunshine microscope. In a number of the plants, stomata are present on stems and other parts of plants. Stomata play a crucial role in gaseous exchange and photosynthesis. They control by transpiration rate by opening and shutting.
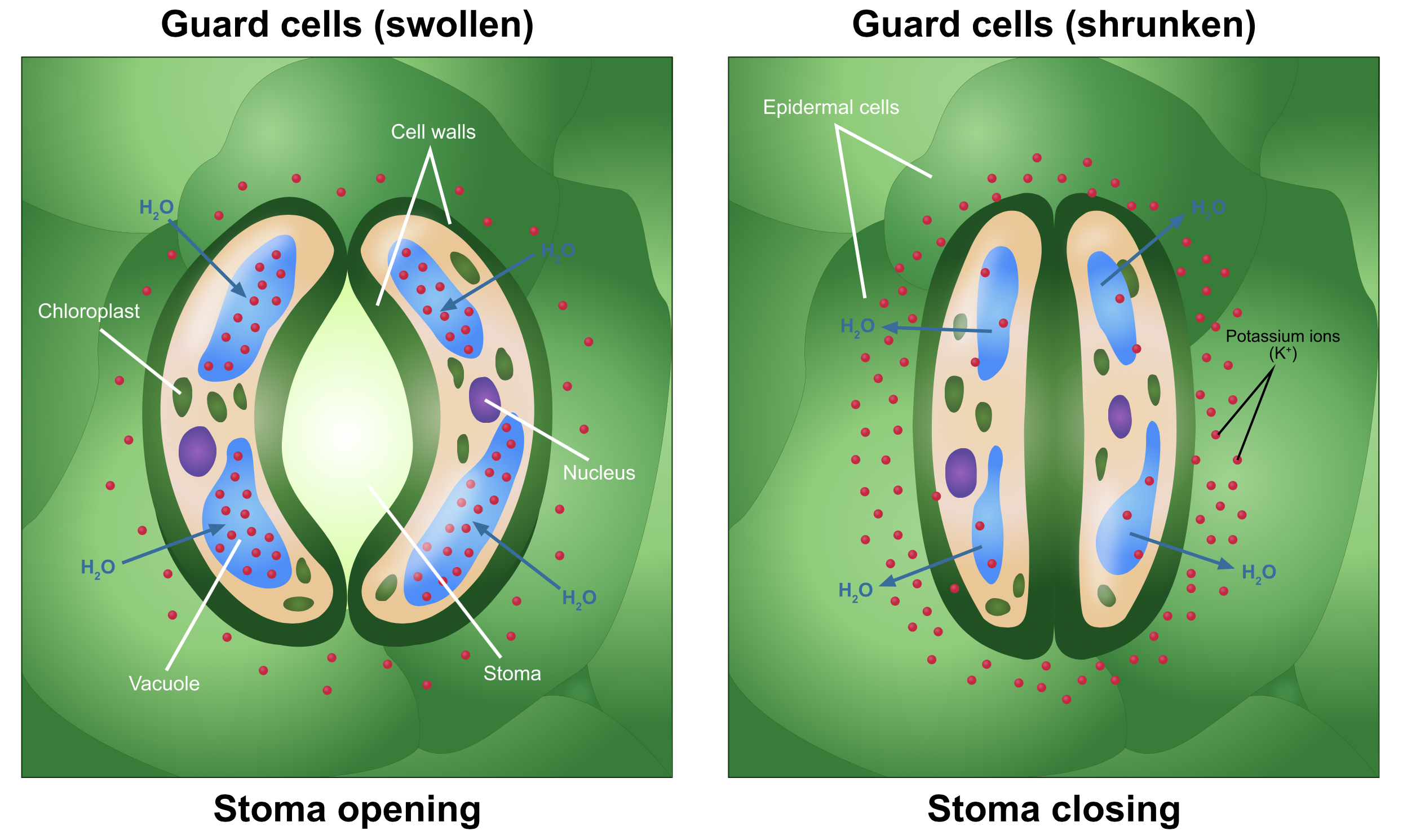
The stomata contain minute pores called stomata surrounded by a pair of guard cells. Stomata, open and shut consistent with the turgidity of guard cells. The cell membrane surrounding the pore is hard and versatile. The form of guard cells usually differs in both monocots and dicots, though the mechanism continues to be an equivalent. Guard cells are bean-shaped and contain chloroplasts. They contain chlorophyll and capture light energy.
The subsidiary cells surround the guard cells. they're the accessory cells to protect cells and are found within the epidermis of plants. they're present between guard cells and epidermal cells and protect epidermal cells when the guard cells expand during stomatal opening.
The mechanism of stomatal opening and closure-
The opening and shutting of stomata depend upon the turgor pressure, caused by the osmotic flow of water within the guard cells. When the guard cells are turgid, they expand leading to the opening of stomata. When the guard cells lose water, they become flaccid resulting in stomatal closure. Stomata normally open when the sunshine strikes the leaf and shut during the night.
Factors Affecting Stomatal Movement:
The most prominent factors that affect stomatal movement (opening and shutting of stomata) include:
(i) Light,
(ii) Temperature,
(iii) Water availability to plants, and
(iv) (CO2) concentration.
Note: Cobalt chloride test: This method is employed for the comparison of transpiration from the both surfaces of the leaves. It's first of all shown by Stall. The main reason for the pressure of the opened stomata is that the K-Dur 20 or potassium malate. The parameter is employed to seek out the world of the stomata on the leaf.
