Question
Question: Explain the mechanism of DNA replication....
Explain the mechanism of DNA replication.
Solution
DNA replication seems to be semi conservative, which means that each DNA double helix strand serves as a template for synthesizing a new, complementary strand.
Complete Answer:
- While we all know that DNA is the genetic code which allows our cells to grow and replicate in a planned manner. Because of this the 'Blueprint of Life' is named.
- DNA is the genetic material which defines body cells. For a cell to replicate and divide into its daughter cells, biomolecules and organelles must first be copied and dispersed among all cells. The DNA consists of four nucleotides, referring to its structure.
- These nucleotides are molecules consisting of a group of phosphates, a sugar ring and nitrogenous base. Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) are nucleotides. A and G are called Purines while Pyrimidines are T and C.
- DNA consists of two strands. These strands include nucleotides set up one after the other and those nucleotides are connected to the other strand nucleotides.
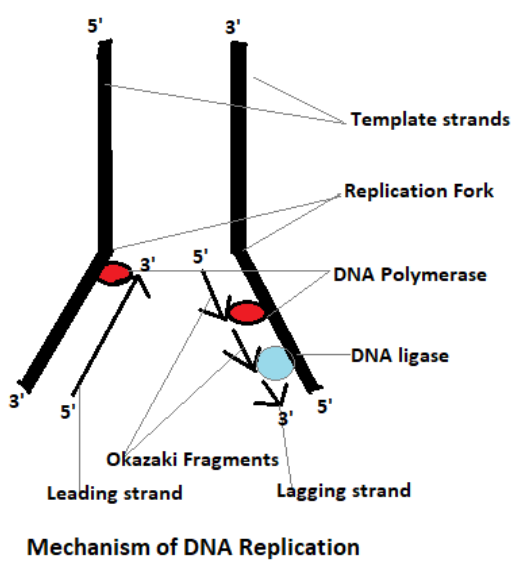
Initiation, elongation and termination are three primary steps in replication of DNA.
- In the 1st step i.e., initiation is the step where replication starts. The place where the replication starts is called the Origin of Replication (oriC). Helicase carries the process of strand separation, which contributes to replication fork formation.
- In the 2nd step i.e., elongation, the DNA Polymerase III enzyme forms the new strand by analyzing the nucleotides on the template strand and inserting one nucleotide after another in particular. If the template has an Adenine (A), it will only insert a Thymine (T) to the new strand.
- In the 3rd step i.e., termination, as Polymerase III attaches nucleotides to the lagging strand and produces fragments of Okazaki which form when it sometimes leaves a gap or two between the fragments. Ligase covers the gaps. It also removes nicks in double-stranded DNA.
Note: One of the most significant DNA Replication principles is that it is a semi-conservative operation. This means that each double helix in an organism's new generation forms an "old" strand, and a "new" strand twisted around each other.
