Question
Question: Explain the interphase of the cell cycle with the help of a diagrammatic view....
Explain the interphase of the cell cycle with the help of a diagrammatic view.
Solution
Cell cycle is the Process in which one cell divides into two daughter cells having the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Interphase is the phase where a cell starts its growth and replicates its genome content.
Complete answer:
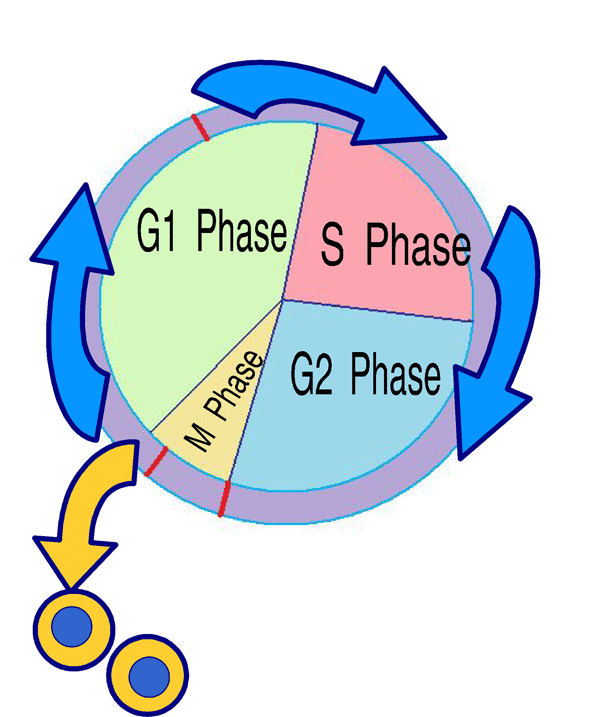
Cell cycle is a process of sequenced events that occurs in a cell where it undergoes different physical and biological changes and a single cell ultimately results in two daughter cells. Cell cycle consists of four major stages or steps: G1-phase, S-phase, G2-phase and M-phase. Initial three stages, G1-phase, S-phase and G2-phase are combined called as interphase.
Interphase starts with G1 or Gap1 phase and the cell accumulates all the necessary protein and growth factors essential for next stages of cell division. Cells undergo different biosynthetic processes and duration of this phase can vary according to the environmental factors and different organisms and different types of cells within the same organism.
Next step of interphase is the S-phase or Synthesis phase, in which the stage cell replicates its genetic material and duplicates it. Here the amount of genetic material doubles but the number of chromosomes remains the same as the parent cell.
Next step of interphase is the G2 or Gap2 phase. In this stage, cells synthesize all necessary proteins and factors required for the mitotic phase. And after completion of the G2 phase, the cell goes to M-phase. And completion of the cell cycle completes.
Note: Before moving into M-phase from G2 phase, the cell should pass through a checkpoint which is a regulatory system of cells which ensures the smooth regulation and cell division. It is regulated by the p53 gene which is involved in DNA repair if there is any damage in DNA.
