Question
Question: Explain the formation of molecules with valence bond theory....
Explain the formation of molecules with valence bond theory.
Solution
VBT is the valence bond theory. The theory defines the electronic structures of atoms or molecules. The valence bond theory explains that the electrons fill the atomic orbitals. Also, valence bond theory explains that the nucleus of one molecule is attracted to the electrons of another molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to explain the formation of NH3 molecule with valence bond theory.
The electronic configuration of nitrogen is 1s22s22p3. The nitrogen atom has five valence electrons in its valence shell.
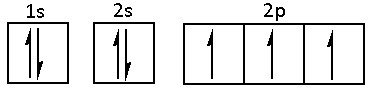
The 2s orbital of nitrogen is completely filled and does not participate in hybridisation. In the 2p orbital, one orbital contains one electron each. Thus, nitrogen atoms have three unpaired electrons.
The electronic configuration of hydrogen is 1s1. The hydrogen atom has one valence electron in its valence shell.
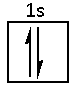
Hence, the three s orbitals of the hydrogen atoms will hybridise with the 2p orbital of nitrogen. Thus, three sigma bonds are formed between nitrogen and hydrogen.
Thus, the shape of ammonia formed will be trigonal pyramidal and the geometry is tetrahedral.
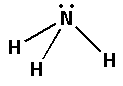
The bond is formed by the overlapping of orbitals. Valence bond theory considers the bonds formed to be polar covalent bonds. The ammonia molecule has three bond pairs and one lone pair of electrons. Thus the hybridisation of ammonia molecules is sp3.
Note: The postulates of valence bond theory are as follows:
- When two valence half-filled orbitals belonging to two different atoms overlap each other covalent bonds are formed. Overlapping increases the electron density in the area between the two bonding atoms. Thus, the stability of the molecule increases.
- The atom can form multiple bonds with other atoms due to the presence of many unpaired electrons. The paired electrons do not participate in bonding.
- The covalent bonds formed are directional and parallel to the overlapping atomic orbitals.
4)The pi bonds are formed by sidewise overlapping of the atomic orbitals and the sigma bonds are formed by the axial overlapping of the atomic orbitals.
