Question
Question: Explain the formation of a triple bond with a diagram....
Explain the formation of a triple bond with a diagram.
Solution
A triple bond is a covalent bond formed by sharing three pairs of electrons. Both the sigma bond and pi-bond are the two types of covalent bonding seen in the formation of multiple bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
A triple bond is made of three bond pairs, that is, three pairs of shared electrons.
Taking an example of the acetylene molecule, having a triple bond between the two-carbon atom, takes place as follows:
-The carbon atom has configuration 2s22p2, having four valence electrons in its ground state. In the excited state, one of the s-orbital electrons moves to the p-orbital.
The s-orbital being non-directional is on the internuclear axis (that is, Z-axis, a line which connects the centre of the nucleus of the two carbon atoms) and the pzorbitals of the carbon is also directed along the internuclear axis.
-Thus, the two orbitals undergo overlapping to form the two sp hybrid orbitals on the carbon atom, having one electron each. One of the sphybrid orbital shares its electron forming a covalent bond with the sphybrid orbital on the adjacent carbon atom, through end-to-end overlapping. Thus, a sigma bond is formed.
The other sp hybrid orbital forms a bond with the s-orbital of the hydrogen atom.
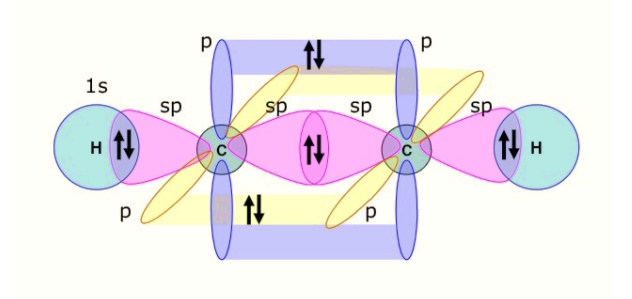
-We are left with the pxandpy unhybridized orbitals with one electron each. These two are perpendicular to the internuclear axes. Thus, involving sideways overlapping of the pxandpy orbitals with the pxandpy of the adjacent carbon atom. Thus, forming two pi-bonds.
Therefore, a triple bond is formed in the acetylene molecule with two pi-bonds and one sigma bond.
Note: The hydrocarbons with triple bonds are called alkyne. The triple bond formation leads to an increase in bond strength, decrease in bond length, linear structure and increase in the melting and boiling point.
