Question
Question: Explain the following at least one example : Cannizzaro’s reaction...
Explain the following at least one example : Cannizzaro’s reaction
Solution
Cannizzaro reaction is a redox reaction in which a hydride is transferred from one substrate molecule to another: one aldehyde is oxidised to form an acid, while the other is reduced to form an alcohol.
Complete answer: When aldehydes without an α- hydrogen are treated with a concentrated alkali solution, they undergo self-oxidation reduction. As a result, one molecule of aldehyde is reduced to the appropriate alcohol, while the other is oxidised to the appropriate acid. The Cannizzaro reaction is the name for this reaction. This reaction occurs in aldehydes that do not contain hydrogen, such as formaldehyde and benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO).
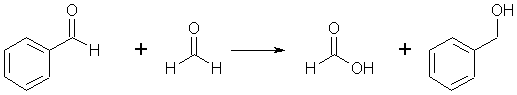
Example: In the presence of concentrated NaOH, two molecules of formaldehyde generate methanol and sodium formate.
HCHO+HCHONaOHCH3OH+HCOONa MethanalMethanolSod.formate
Importance of cannizzaro reaction: Polyols are made from formaldehyde and other aldehydes using a combination of aldol condensation and the crossed-Cannizaro reaction. The preparation of Pentaerythrit from acetaldehyde is a popular application of the reaction. Polyols are very useful and have a wide range of uses in manufacturing.
Note:
The carbanion of 2-methylpropanal is unstable due to the +I-effect of the two alkyl groups bound to the alpha-carbon. In other words, rather than forming the carbanion, 2-methylpropanal tends to be attacked by the OH− ion at the aldehyde, resulting in the formation of cannizzaro products.
