Question
Question: Explain sulphonation of benzene with reaction....
Explain sulphonation of benzene with reaction.
Solution
Sulphonation is a reversible reaction that produces benzenesulfonic acid by adding sulphur trioxide and fuming sulphuric acid. The reaction is reversed by adding hot aqueous acid to benzene sulphonic acid to produce benzene.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, is the mechanism for the electrophilic substitution reaction between benzene and sulphuric acid (or sulphur trioxide)
The electrophilic substitution reaction between benzene and sulphuric acid:
There are two equivalent ways of sulfonated benzene:
→ Heat benzene under reflux with concentrated sulphuric acid for several hours.
→ Warm benzene under reflux at 40∘C with fuming sulphuric acid for 20 to 30 minutes.
C6H6+H2SO4→C6H5SO3H+H2O ------(1)
The formation of the electrophile:-
The sulphur trioxide electrophile arises is one of two ways depending on which out of acid you are using concentrated sulphuric acid contains traces of SO3 due to slight dissociation of the acid.
H2SO4⇌H2O+SO3 --------(2)
Fuming sulphuric acid H2S2O7, can be thought of as a solution of SO3 in sulphuric acid and so is a much richer source of the SO3. sulphur trioxide is an electrophile because it is a highly polar molecule with a fair amount of positive charge on the sulphur atom. It is this which is attracted to the ring electrons.
The electrophilic substitution mechanism:-
Stage one:-
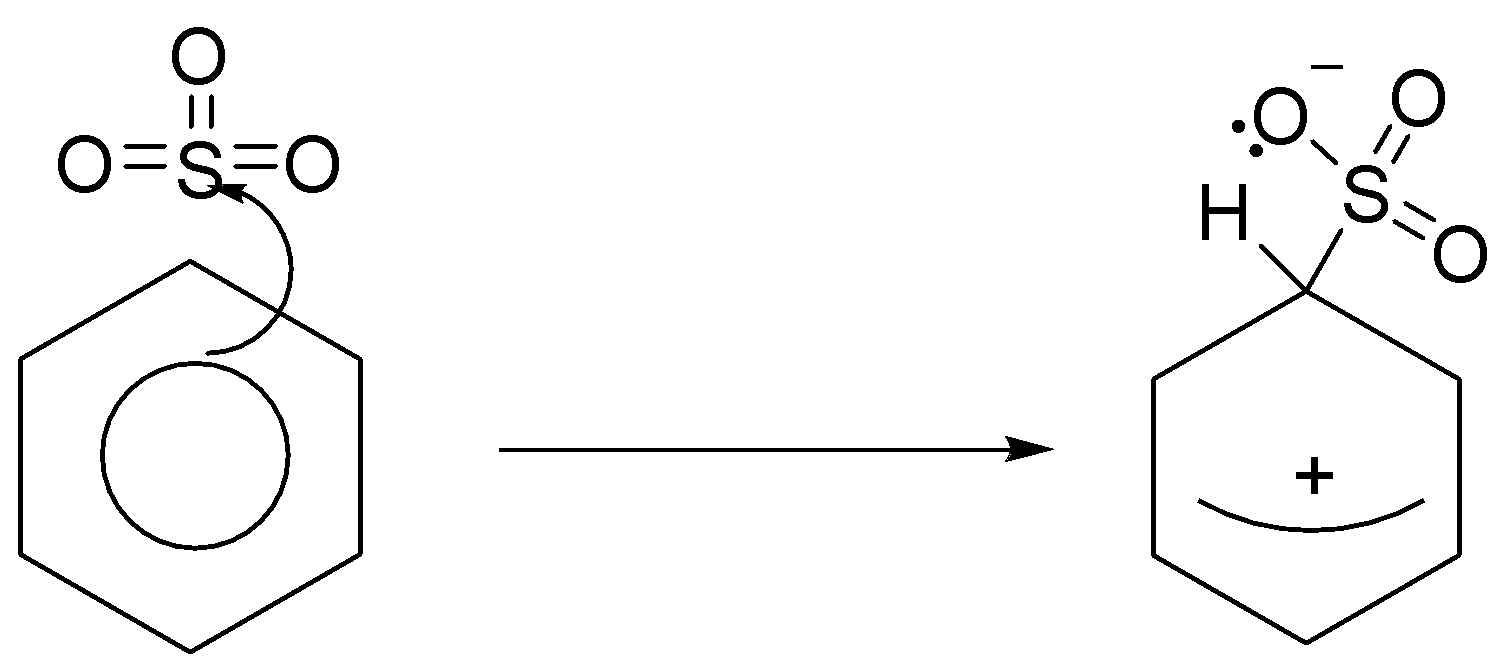
Stage two

The second stage of the reaction involves a transfer of the hydrogen from the ring to the negative oxygen.
Note: The electrophilic substitution reaction of benzene is a three step process involving:-
→Generation of the electrophile
→Intermediate carbocation formation
→Removal of a proton from carbocation intermediate.
