Question
Question: Explain \(S{N^2}\) reaction with one example....
Explain SN2 reaction with one example.
Solution
SN2 reaction is a type of reaction in organic chemistry. It involves the nucleophilic substitution of a reactant on the carbon atom on which the leaving group is present. It is a one step reaction involving the formation of an intermediate.
Complete step by step answer:
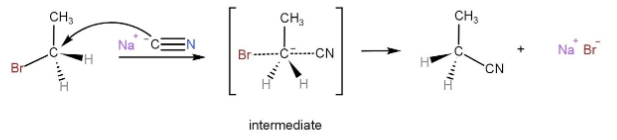
In the SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks on the carbon on which the leaving group is present, where the attack of nucleophile and the elimination of the leaving group is simultaneous.
Since, there are two reacting molecules in a single step therefore, it is called a bimolecular reaction.
The nucleophile attacks from one side and the leaving group is eliminated from the opposite side, due to this inversion in the molecule taking place.
An example of SN2 reaction is,
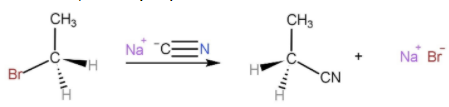
Here, CN− is the attacking nucleophile and Br− is the leaving group.
Mechanism of the reaction is,
Note:
-In SN2 reactions, the order of reactivity of alkyl halides is,
Methyl>1∘>2∘.
-In 3∘ alkyl halides, due to the bulkiness of the molecule, there is steric hindrance and the nucleophile cannot attack. Therefore, 3∘ alkyl halides do not undergo SN2 reaction.
-In methyl groups there is no steric hindrance due to which the attack of nucleophile and elimination of leaving group occurs readily.
-As the crowding on the carbon atom increases as in case of 1∘ and 2∘, the rate of SN2 reaction decreases.
