Question
Question: Explain Rosenmond’s reduction of benzoyl chloride....
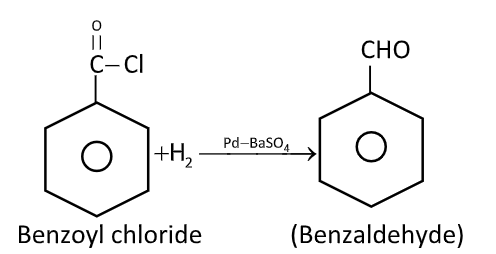
Explain Rosenmond’s reduction of benzoyl chloride.
Solution
Rosenmund’s reduction is a hydrogenation process in which acid chloride is selectively reduced to aldehydes.
Complete step by step answer:
Acyl chlorides can be reduced into aldehydes with hydrogen in boiling xylene using palladium or platinum as catalyst supported on barium sulphate. This reaction is called Rosenmund’s reduction.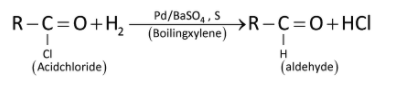
For example:
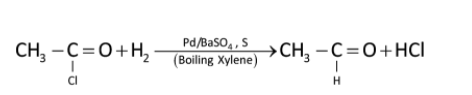
Similarly
The function of BaSO4is to poison the catalyst at the aldehyde stage. The catalyst is also poisoned to small extent by sulphur compounds to prevent further reaction of aldehyde to 1∘ alcohols. Generally, a small amount of quinoline and sulphur is also added.
Note:
Rosenmund’s reduction is only for the preparation of aldehydes but ketones cannot be prepared by this method.
Acid chlorides are readily reduced to aldehydes by weaker reducing agents, like lithium tri – tertiary butoxy aluminium hydride.
