Question
Question: Explain Friedel-Craft alkylation of chlorobenzene. Give an equation....
Explain Friedel-Craft alkylation of chlorobenzene. Give an equation.
Solution
Hint : An alkyl group can be added to a benzene molecule by an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction called the Friedel‐Crafts alkylation reaction. One example is the addition of a methyl group to a benzene ring. The mechanism for this reaction begins with the generation of a methyl carbocation from methyl bromide.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation refers to the replacement of an aromatic proton with an alkyl group. This is done through an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring with the help of a carbocation. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction is a method of generating alkyl benzenes by using alkyl halides as reactants.
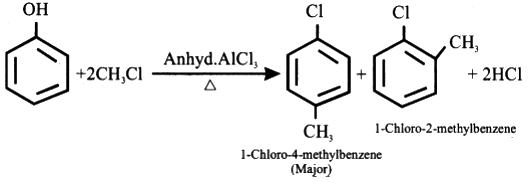
A Lewis acid catalyst such as FeCl3 or AlCl3 is employed in this reaction in order to form a carbocation by facilitating the removal of the halide. The resulting carbocation undergoes a rearrangement before proceeding with the alkylation reaction.
Additional Information:
Mechanism:
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction proceeds via a three-step mechanism.
Step 1
The Lewis acid catalyst ( AlCl3 ) undergoes a reaction with the alkyl halide, resulting in the formation of an electrophilic carbocation.
Step 2
The carbocation proceeds to attack the aromatic ring, forming a cyclohexadienyl cation as an intermediate. The aromaticity of the arene is temporarily lost due to the breakage of the carbon-carbon double bond.
Step 3
The deprotonation of the intermediate leads to the reformation of the carbon-carbon double bond, restoring aromaticity to the compound. This proton goes on to form hydrochloric acid, regenerating the AlCl3 catalyst.
Note :
Friedel craft alkylation will undergo that aromatic compound, which is electron-rich. As it is the electrophilic substitution reaction. But, since the carbo-cations formed by aryl and vinyl halides are extremely unstable, they cannot be used in this reaction. And also the presence of a deactivating group on the aromatic ring can lead to the deactivation of the catalyst due to the formation of complexes.
