Question
Question: Explain Clemmensen’s reduction with an example....
Explain Clemmensen’s reduction with an example.
Solution
Clemmensen’s reduction reaction is named after Erik Christian Clemmensen who was a Danish chemist. In Clemmesen’s reduction, the reduction process takes place in aldehydes or ketone in the presence of catalyst and acid. This reaction is mostly effective for the reduction of cyclic ketone.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction where reduction of ketones or aldehydes takes place to form an alkane with the help of hydrochloric acid and zinc amalgam is known as Clemmensen’s reduction reaction.
In other words, In Clemmensen Reduction, deoxygenation of aldehyde or ketones takes place to form a hydrocarbon.
The general Clemmensen’s reduction reaction is shown below.
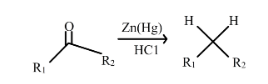
Example:
The reduction of phenyl ethanone to 1-phenyl ethane is shown below.
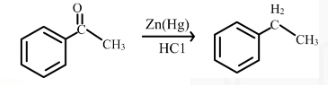
In this reaction phenyl ethanone reacts with hydrochloric acid and zinc amalgam to form 1-phenyl ethane.
The mechanism of the reaction is not till completely understood but based on the observations, there are two proposals,
According to the Carbenoid mechanism which is a radical process, the reduction process takes place at the surface of the zinc catalyst. Alcohols containing groups are not suggested as an intermediate because when the alcohols are used in the same conditions it does not lead to the formation of alkane.
According to the carbanionic mechanism, the zinc attacks the protonated carbon directly.
Note:
In Clemmensen reduction, the substrate used should be stable to strong acids. The Clemmensen reduction reaction is complementary with the Wolff-Kishner Reduction. In Wolff-Kishner reaction strong basic condition is used to carry out the reaction.
