Question
Question: Explain and derive equivalent Resistance formula for 3 Resistors connected in Pure series. Generaliz...
Explain and derive equivalent Resistance formula for 3 Resistors connected in Pure series. Generalize the formula?
Solution
When three resistors are concealed in derives then the same current passes through each resistor but the voltage drop is different for each resistor.
Complete step by step solution:
According to Ohm’s formula V = IR.
When three resistors are connected in series then the same current passes through each resistor but the voltage drop is different for each resistor. If V is the applied voltage and V1,V2 and V3 is voltage across resistance R1,R2andR3 respectively then.
V=V1+V2+V3 …(1)
According to ohm’s law
V = IR
∴ IReq=IR1+IR2+IR3
IReq=I(R1+R2+R3)
Req=R1+R2+R3
So, the equivalent resistance or the total resistance of the circuit can be defined as a single value of resistance that can replace any number of resistors connected in series without altering the value of the current or the voltage of the circuit.
If we have n resistance connected in series, then generalized formula for equivalent resistance is
Req=R1+R2+R3.......+Rn
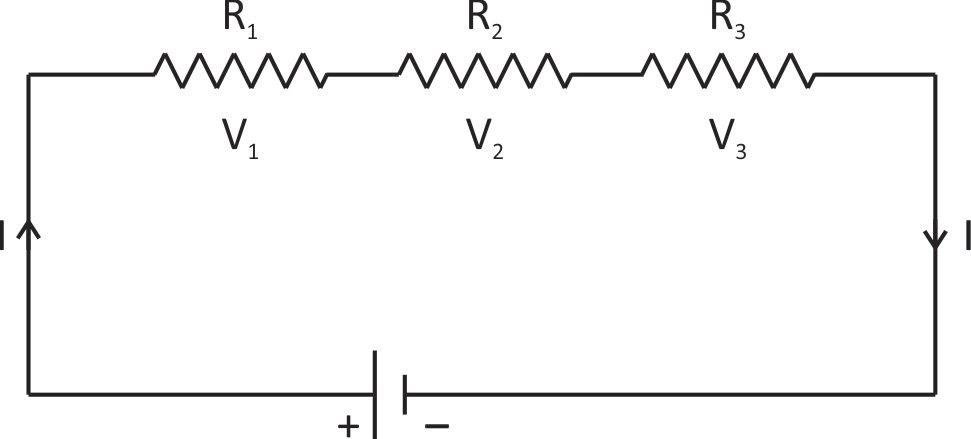
We know that applied voltage is (v)
∴V=V1+V2+V3
We also know that
V = IR (from ohm’s law)
∴IReq=IR1+IR2+IR1
⇒IReq=I(R1+R2+R3)
⇒R1+R2+R3
So, the equivalent resistance or the total resistance of the circuit can be defined as a single value of resistor connected in series with altering the values of the current or voltage in the circuit.
Note: If three or more resistors with the same value are connected in parallel, then the equivalent resistance is equal to nR.
