Question
Question: Excess \[KCN\] is added to a solution of \[CuS{O_4}\] during the process of confirmation of \[Cu\] i...
Excess KCN is added to a solution of CuSO4 during the process of confirmation of Cu in the presence of Cd in group2 . Pick out the correct statement with regards to the products formed.
This question has multiple correct options
A. K2[Cu(CN)4] is formed as the main product.
B. (CN)2is one of the products obtained.
C. The main product is diamagnetic.
D. The hybridization of Cu in the product is sp3 .
Solution
Both the Cu2+and Cd2+cation form insoluble sulfides when treated with H2S in acidic medium. The confirmatory test is achieved by treating the solution containing Cu2+ ion with KCN which forms a stable complex.
Complete step by step answer: The problem deals with the qualitative estimation of inorganic cations. After the removal of group 1 cations, the clear acidic solution is treated with H2S gas or Na2S solution. The group 2 cations are precipitated as sulfides under the given reaction conditions.
The precipitated sulfides of various cations have characteristic colors. The color of copper sulfide is black and the color of cadmium sulfide is yellow. The indication of the color gives a preliminary test for the presence of the cation.
The confirmatory test for the presence of Cu2+ ion is achieved by treating copper solution with excess KCN. The reaction of KCN and given solution of CuSO4 occurs in a stepwise manner. The sequence of reaction begins with the formation of cuprous cyanide and cyanogen gas.
The cuprous cyanide thus formed is unstable and dissolves in excess of KCN. The reaction is as follows:
CuSO4+2KCN→Cu(CN)2+K2SO4
2Cu(CN)2→2CuCN+CN−CN
CuCN+3KCN→K3[Cu(CN)4]
Let us check the correctness of the given statements one by one.
A. K2[Cu(CN)4] is formed as the main product. This is incorrect statement as the main product is K3[Cu(CN)4] and not K2[Cu(CN)4]. The CuCN formed reacts with KCN to produce K3[Cu(CN)4].
B. (CN)2 is one of the products obtained. This is a correct statement as cuprous cyanide produced in the first step is unstable and undergoes decomposition to generate (CN)2 gas as one of the products of the reaction.
C. The main product is diamagnetic.
The main product is K3[Cu(CN)4]. The central metal ion is copper. Copper is an element in the periodic table with atomic number29. Its electronic configuration is[Ar]3d104s1. The oxidation state of copper in K3[Cu(CN)4] is +1. The electron configuration is [Ar]3d10. The d orbitals are completely filled and all the electrons are paired. There is no unpaired electron. Thus the product is diamagnetic.
D. The hybridization of Cu in the product issp3.
In the +1 oxidation state of copper the inner d orbitals i.e. 3dorbitals are filled up. The outer 4s and 4p orbitals are available for coordination with cyanide ligand. Thus the four cyanide ligands enter into the 4s and 4p orbitals. Thus the hybridization of Cu is sp3.
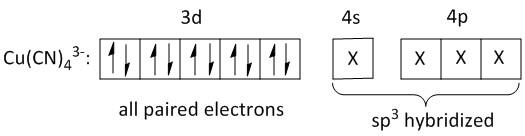
Hence statements B, C and D are correct.
Note: The similar complex formed with Cd is unstable, i.e.K3[Cd(CN)4]. The complex product formed in this reaction is an anionic complex. The primary valency is satisfied by potassium ion and the secondary valency is satisfied by cyanide ion.
