Question
Question: Evaluate the area of the ellipse \(\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{9}=1\) above the x-axis....
Evaluate the area of the ellipse 4x2+9y2=1 above the x-axis.
Solution
Hint: Plot the curve on a graph. Observe that the curve is symmetrical in all the four quadrants. Hence find the area in the first quadrant, and hence the area of the ellipse will be two times the area in the first quadrant(Because only the first quadrant and the second quadrant are above x-axis). For finding the area in the first curve quadrant express y in terms of x. Note that y>0 and hence take only the positive sign. Then use the fact that the area under the curve is given by ∫abydx. Substitute suitable values of a and b and integrate and hence find the area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
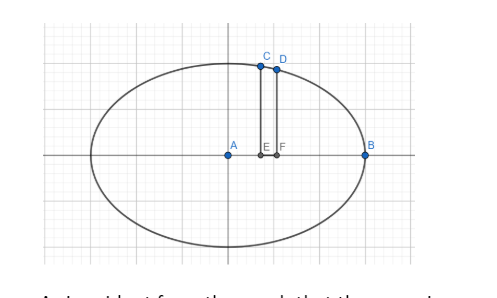
As is evident from the graph that the curve is symmetrical in the four quadrants. Hence, we will find the area in the first quadrant, and then the total area will be two times the area in the first quadrant.
Now, we have
4x2+9y2=1
Subtracting 4x2 from both sides, we get
9y2=1−4x2
Multiplying both sides by 9, we get
y2=9(1−4x2)
Hence, we have
y=±31−4x2=±234−x2
Now since in the first quadrant, y>0.
Hence, we have
y=234−x2
Now consider the vertical strip CDEF.
Here CE = y and EF = dx
Hence the area of the strip will be ydx.
The area in the first quadrant will be the sum of the area of these vertical strips from A to B.
Now at point B, we have y = 0
Hence 4x2=1⇒x2=4⇒x=±2
Since the abscissa of point B is positive, we have x=2.
Hence the area in the first quadrant will be ∫02ydx
Substituting the value of y, we get
The area in the first quadrant is ∫02234−x2dx
Let I=∫02234−x2dx
Finding the value of I:
Put x = 2sint.
Differentiating both sides with respect to t, we get
dtdx=2costdt⇒dx=2costdt
When x = 0, we have 2sint=0⇒sint=0⇒t=0
When x = 2, we have 2sint=2⇒sint=1⇒t=2π
Hence we have
I=23∫02π4−4sin2t2costdt=6∫02π1−sin2tcostdt
Now, we know that 1−sin2t=cos2t
Hence, we have
I=6∫02πcos2tcostdt=6∫02π∣cost∣costdt
Since in the interval (0,2π) cost is positive, we have ∣cost∣=cost
Hence, we have
I=6∫02πcos2tdt (i)
We know that ∫abf(x)dx=∫abf(a+b−x)dx
Hence, we have
I=6∫02πcos2(2π−x)dx
We know that cos(2π−x)=sinx
Hence, we have
I=6∫02πsin2xdx (ii)
Adding equation (i) and equation (ii), we get
2I=6∫02π(sin2t+cos2t)dt
We know that sin2t+cos2t=1
Hence, we have
2I=6∫02π1dt=6t∣02π=6(2π−0)=3π
Dividing both sides by 2, we get
I=23π
Hence the area in the first quadrant is 23π
Hence the total area of the ellipse is 2×23π=3π
Note: [1] We can directly solve I using the fact that ∫a2−x2=2xa2−x2+2a2sin−1ax
Hence, we have
I=23(2x4−x2+24sin−12x0a)=23[(224−4+24sin−122)−(204−02+24sin−120)]=23π
Which is the same as obtained above.
[2] Alternatively, we have
Area of ellipse =πab
Hence the total area of the ellipse π(3)(2)=6π
Hence the area above the x-axis =26π=3π
