Question
Question: Ethyl chloride to ethanal....
Ethyl chloride to ethanal.
Solution
To solve this question, we need to first understand about the nature and properties of the major reactant, i.e. ethyl chloride and the major product, i.e. ethanal. Then we need to understand the changes observed from the reactant to the product and then accordingly form a corresponding chemical equation.
Complete step by step answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Ethyl chloride can be generally classified into the category of alkyl halides. Alkyl halides contain one alkane molecule, in which one of the hydrogen atoms is substituted with a halogen atom. In this case, the parent chain alkane is ethane. To form ethyl chloride, a hydrogen atom is replaced from the two carbon atoms, to attach a chlorine atom to form the final compound. The molecular structure of ethyl chloride can be given as:
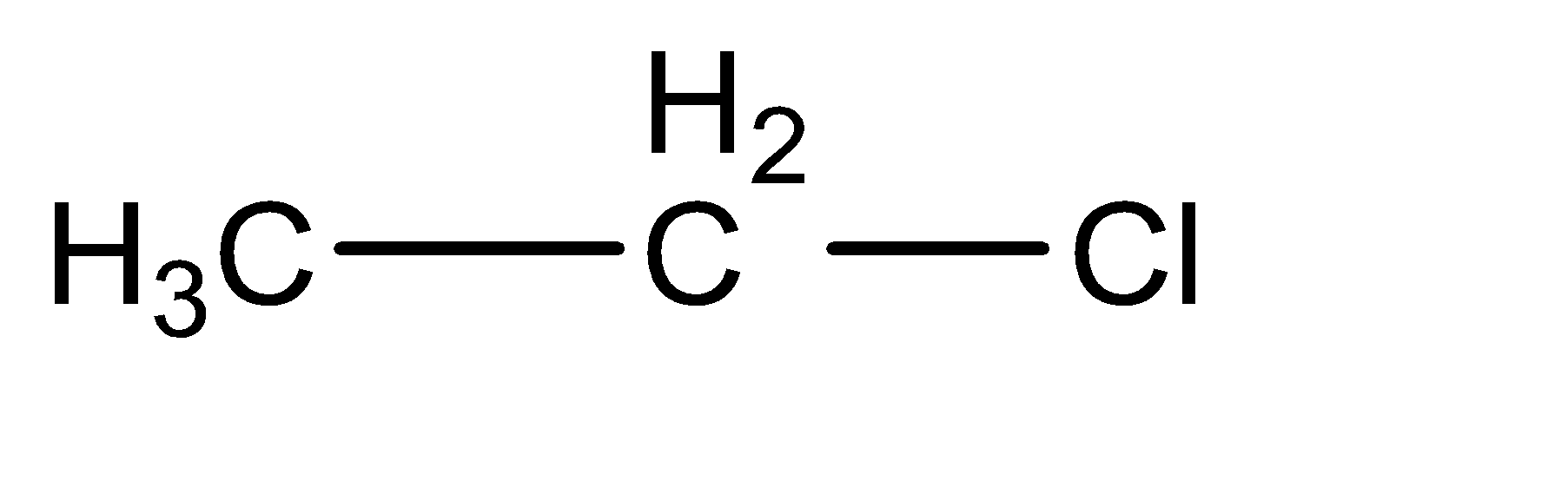
Ethanal can be identified as an aldehyde with two carbon atoms. The molecular structure for ethanal can be given as follows:
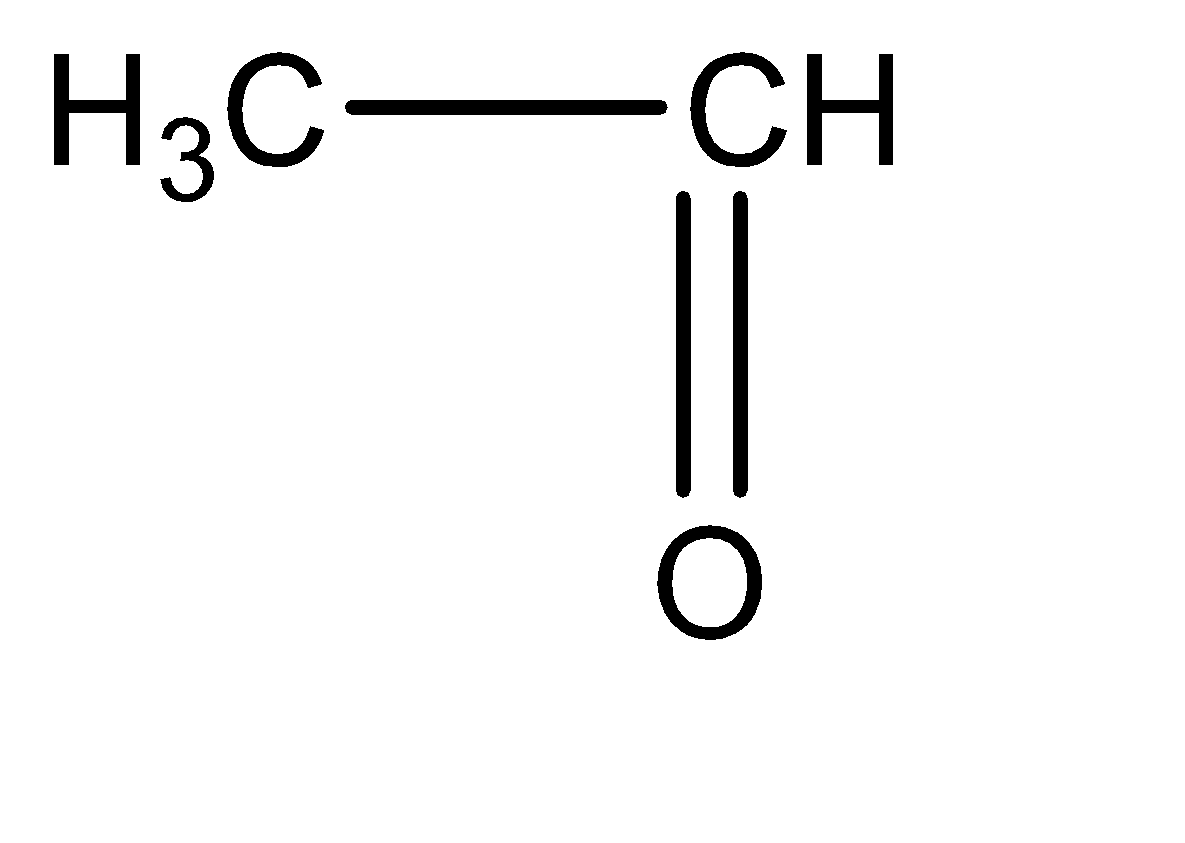
The changes that we can observe between these two molecules are:
1.Chlorine atom is removed
2.One hydrogen atom from the terminal carbon is also removed
3.Terminal carbon is doubly bonded with an oxygen atom.
Hence, to form ethanal from ethyl chloride, we can implement the following steps:
a)Removal of Chlorine atom:
The chlorine atom from ethyl chloride can be done by dehydrohalogenation reaction. This reaction involves reacting alkyl halides with alcoholic KOH to eliminate H-X molecules from the compound. This results in the formation of an alkene.
CH3CH2Clalc.KOHH2C=CH2+HCl
b)Addition of oxygen atom:
Addition of oxygen atom to the compound can be done by hydrogenation of alkene to form alcohol.
H2C=CH2H2OCH3CH2OH
c)Formation of carbonyl group:
The carbonyl group can be formed by removal of a hydrogen molecule. This reaction can be done by using PCC.
CH3CH2OHPCCCH3CHO+H2
Hence, this is the entire process for the formation of ethanal from ethyl chloride.
Note: Studies on animals show that breathing ethanal can severely damage the lungs and cause cancer. Repeated exposure to ethanal in the air may cause cancer in humans. When you drink alcohol, your liver turns ethanal into an acid.
