Question
Question: Establish the relation amongst u, v and f for concave lens....
Establish the relation amongst u, v and f for concave lens.
Solution
We will use the formula for refraction at spherical surfaces here twice. First with the original object at the left side of the lens and then taking the image formed as the virtual object on the right side of the lens to get the result.
Formula used:
refraction at spherical surfaces
vn2−un1=Rn2−n1
Complete step-by-step answer:
We will use the formula for refraction at spherical surfaces on the left side first. Here the medium 2 will be the glass of the lens and medium 1 will be air. Let vo be the distance of the image formed after the first refraction.
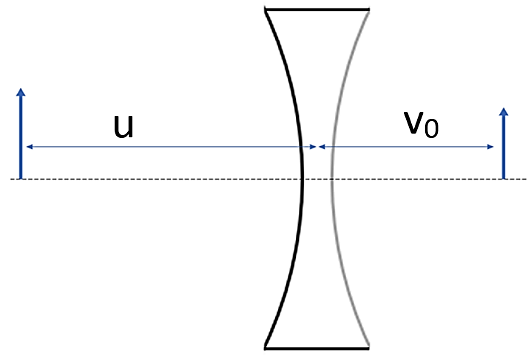
von−u1=−Rn−1
Negative sign on R appears here because the radius of curvature is towards the left of the lens.
For the second reflection, vo will be the distance of the object and v will be the distance of image from the lens.
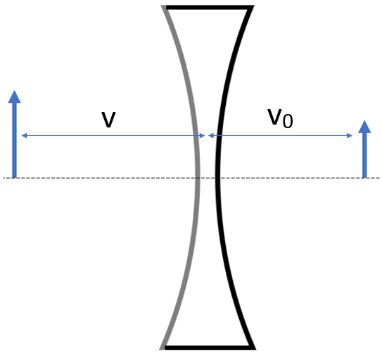
The equation will now be
v1−von=R1−n.
If we add both these equations, we get the final equation as
(von−u1=−Rn−1)+(v1−von=R1−n)⇒v1−u1=R2(1−n)
Then we have gotten a relation with v and u in it. However, we also need to include f. If you remember, if an object was at infinity its image will be formed at the focus of the lens. When we put u=∞in this equation the u1 term becomes zero and we get v1=R2(1−n). Now here v must be equal to f so the quantity on the right of the equals to sign is the inverse of focal length. So, we get the final relation between v, u and f as v1−u1=f1.
Note: The sign convention must be used properly when using these equations. Any sign convention can be chosen but it must remain the same throughout the calculations. Most commonly used and widely accepted sign convention is considering the object to the left of the lens as negative and to the right as positive. The focal length of a concave mirror is negative in this sign convention.
