Question
Question: Enzyme catalyzing optical or geometrical rearrangement of atomic groupings without altering molecula...
Enzyme catalyzing optical or geometrical rearrangement of atomic groupings without altering molecular weight or number of atom is
A. Ligase
B. Isomerase
C. Oxidoreductase
D. Hydrolase
Solution
All living beings have chemical and metabolic reactions occurring within their bodies. These reactions include digestion of food, absorption of molecules, and production of energy. A biochemical reaction is a term used to refer to chemical reactions occurring within the body. Metabolism on the other hand is a combination of all biochemical reactions. Catabolism and anabolism (synthesis) are part of metabolism. Catabolism refers to the breakdown of substances, whereas anabolism refers to the formation of substances.
Step by step answer: The biochemical reactions occurring within the body is catalyzed by globular proteins called enzymes. They only act by catalyzing the chemical reaction and do not undergo any changes themselves. A particular reaction and substrate have a specific enzyme. The enzymes are named based on the reaction or compound they participate in. Enzymes are often termed as biocatalysts. For instance, the hydrolysis of maltose to glucose is catalyzed by the enzyme maltase.
C12H22O11maltase2C6H12O6
MaltosemaltaseGlucose
-Ligase: Ligase can be defined as an enzyme that can be utilized to catalyze the fusion of two large molecules by the formation of a new chemical compound. This is usually accompanied by hydrolysis. Ligases such as DNA ligase are enzymes that are utilized in molecular biology laboratories where these enzymes assist in recombinant DNA experiments including DNA replication, DNA repair, and joining DNA fragments. This is achieved by the catalyzed formation of a phosphodiester bond.
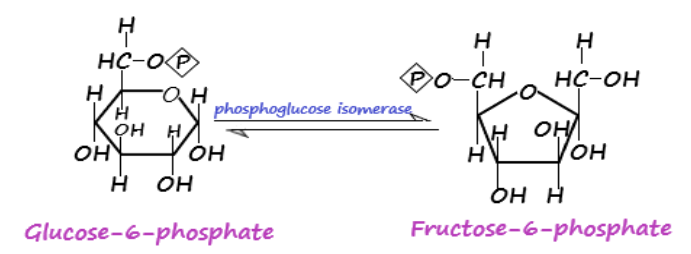
-Isomerase: Enzyme that assists in the conversion of a molecule from one isomer to another with the end product having the same molecular formula but different spatial arrangements are called isomerase. Intramolecular rearrangements involve the breaking and formation of bonds. This is facilitated by isomerases. For instance, the glycolysis process involves the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate in presence of phosphoglucose isomerase catalyst.
-Oxidoreductase: Transfer of electrons from the reductant to the oxidant is catalyzed by the enzyme oxidoreductase. The reductant is also known as an electron donor, while oxidant is referred to as the electron acceptor. Oxidoreductase enzymes utilize cofactors such as NADP or NAD+.
-Hydrolase: Hydrolase is a biochemical catalyst designed to break a chemical bond through hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is defined as the addition of a water molecule to a chemical process. This results in the breakdown of larger molecules to smaller compounds or molecules.
Therefore the correct option is B, i.e., Isomerase
Note: For the progress of a chemical or biochemical reaction, only a small amount of enzyme is required. Enzymes are believed to decrease the activation energy’s magnitude. For instance, acid hydrolysis of sucrose requires activation energy of 6.22 kJ/mol, but when hydrolyzed using sucrase enzyme, the activation energy is 2.15 kJ/mol.
