Question
Question: Energy profile diagram of dehydration of 2-butanol using conc. \({{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\) is given belo...
Energy profile diagram of dehydration of 2-butanol using conc. H2SO4 is given below. Product (b) of the above reaction is:
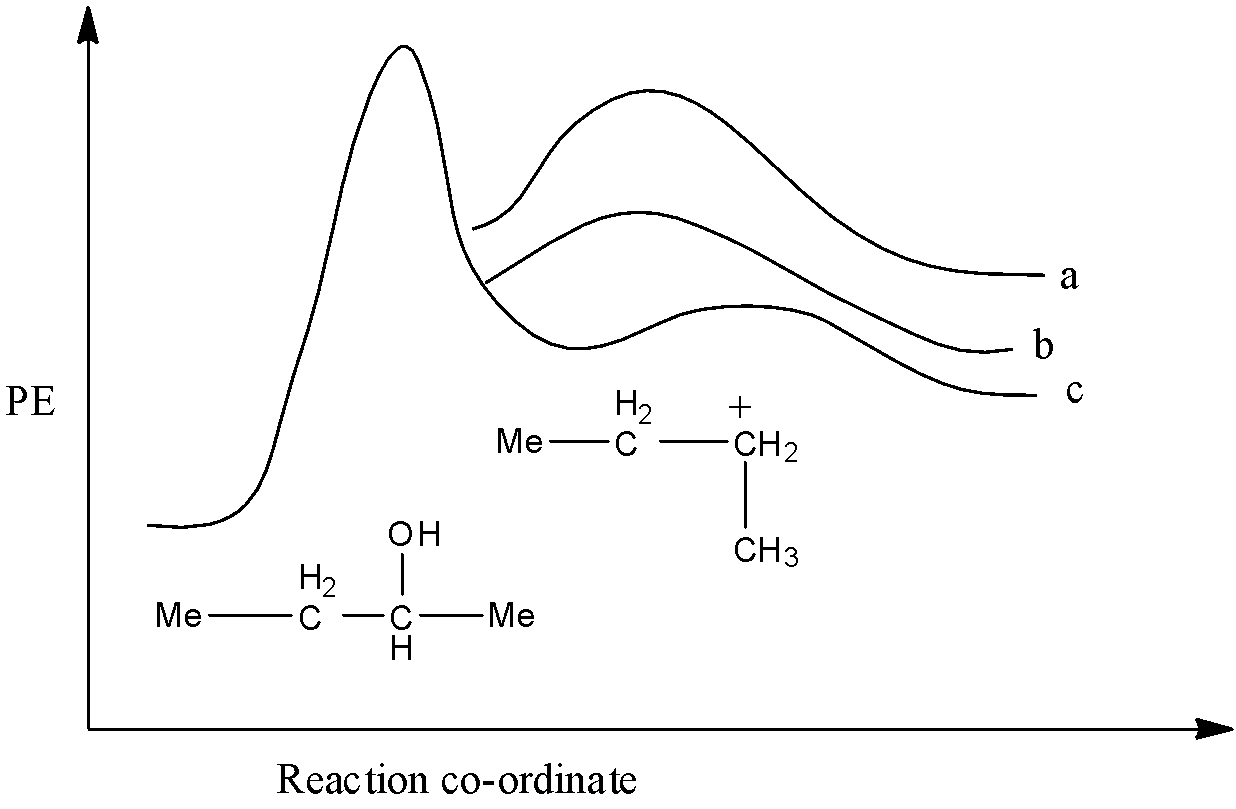
(a)- 1-Butene
(b)- Cis 2-butene
(c)- Trans 2-butene
(d)- Isobutene
Solution
When alcohol is dehydrated using concentrated sulfuric acid then there is the formation of alkene, since 2-butanol is a secondary alcohol, so there will be the formation of three products. The compound that will have high stability will have low potential energy and the compound that will have low stability will have high potential energy.
Complete answer:
The given compound in the question is alcohol, i.e., 2-butanol. It is treated with concentrated sulfuric acid. When alcohol is dehydrated using concentrated sulfuric acid then there is the formation of alkene.
The structure of 2-butanol is given below:
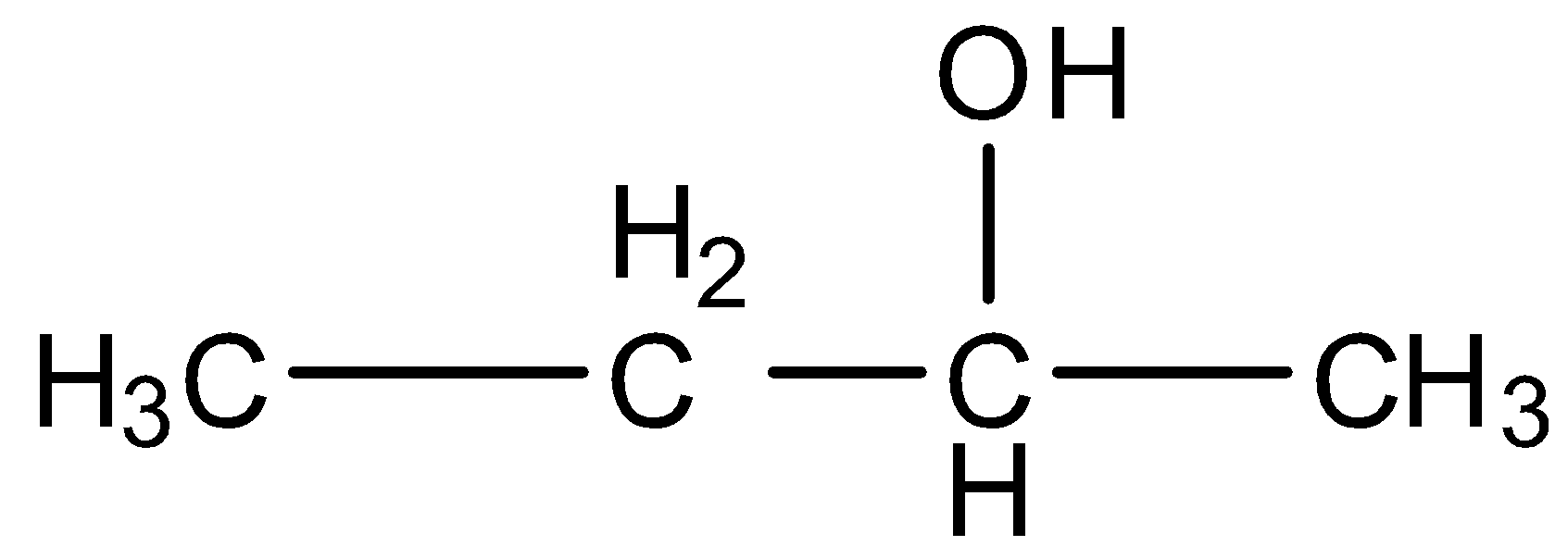
When 2-butanol reacts with concentrated acid then the hydrogen ion will attack the hydroxyl and then there will be the elimination of water molecules from the compound. So, there will be the formation of a carbocation. The reaction is given below:
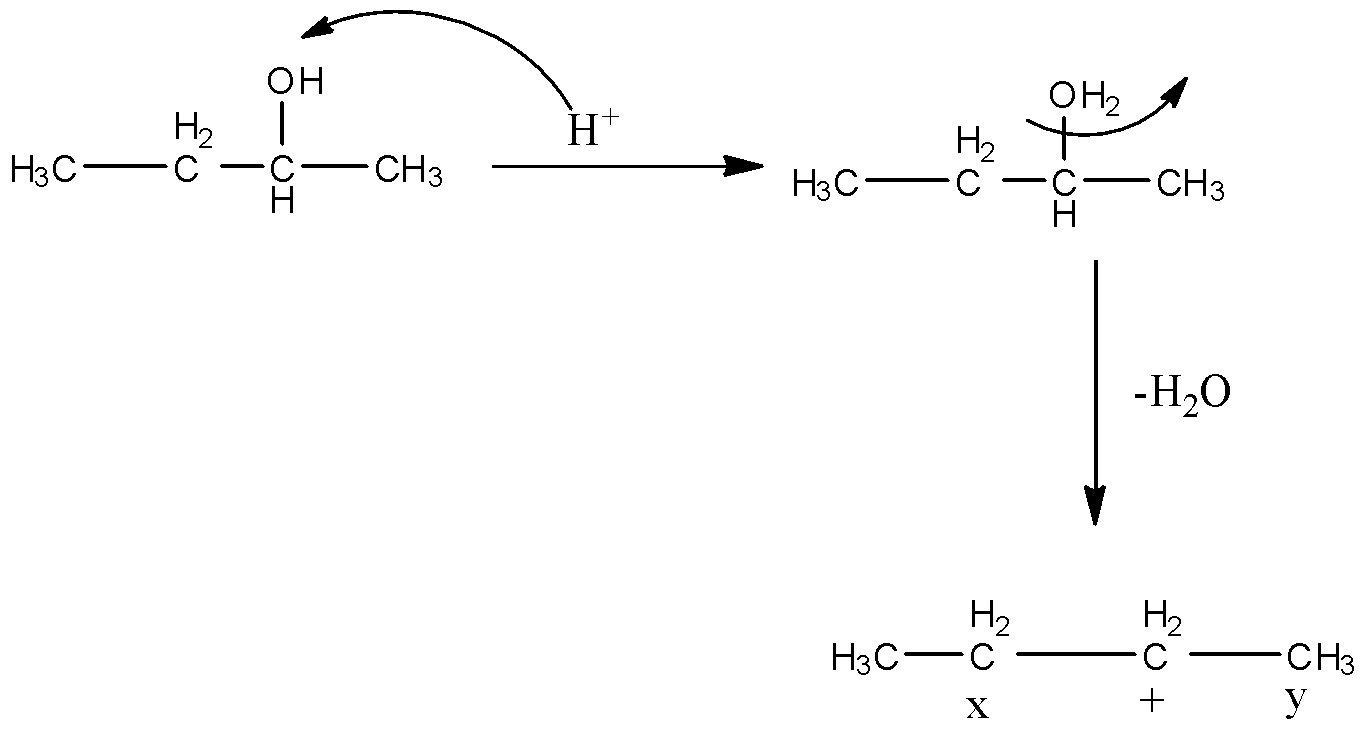
So, there are two positions from which the hydrogen atom can be removed for the formation of alkene. When the hydrogen atom is removed from the x position then there will be the formation of 2 products, i.e., cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene. The structures are given below:
Cis-2-butene
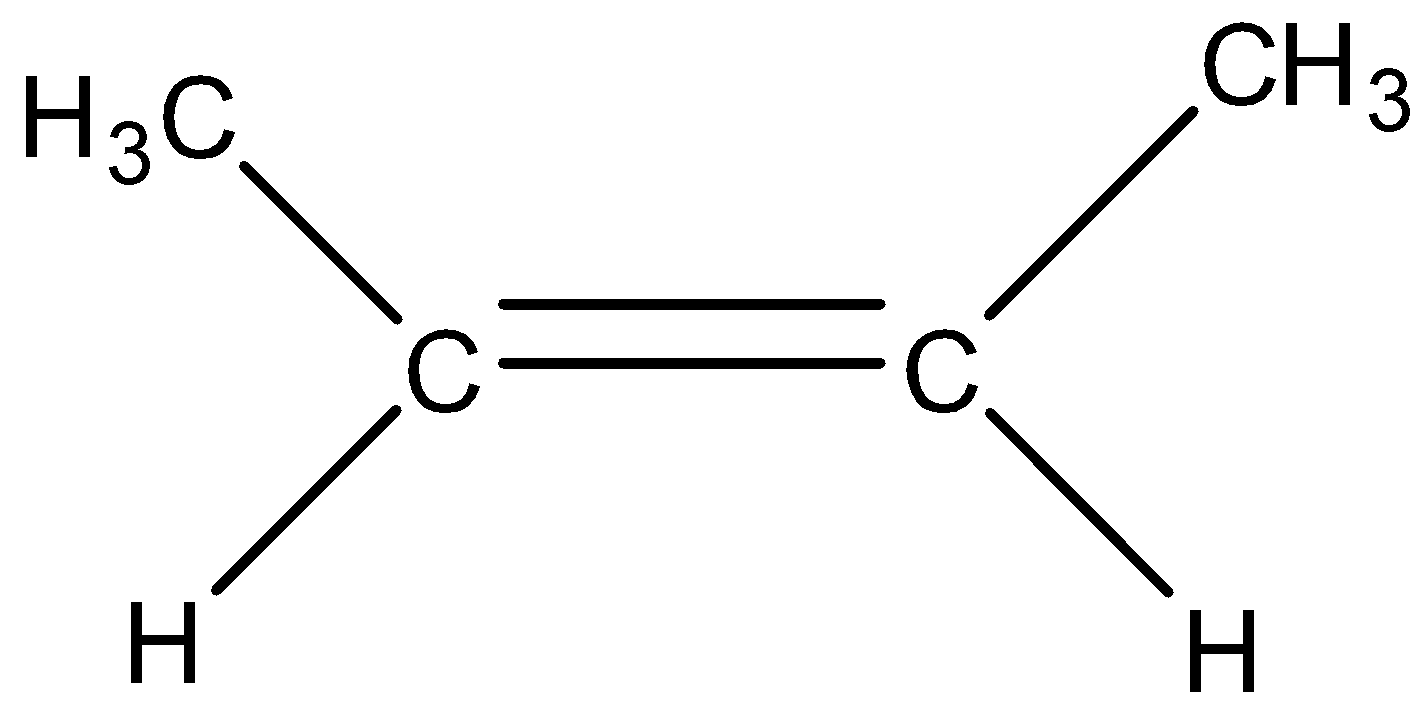
Trans-2-butene
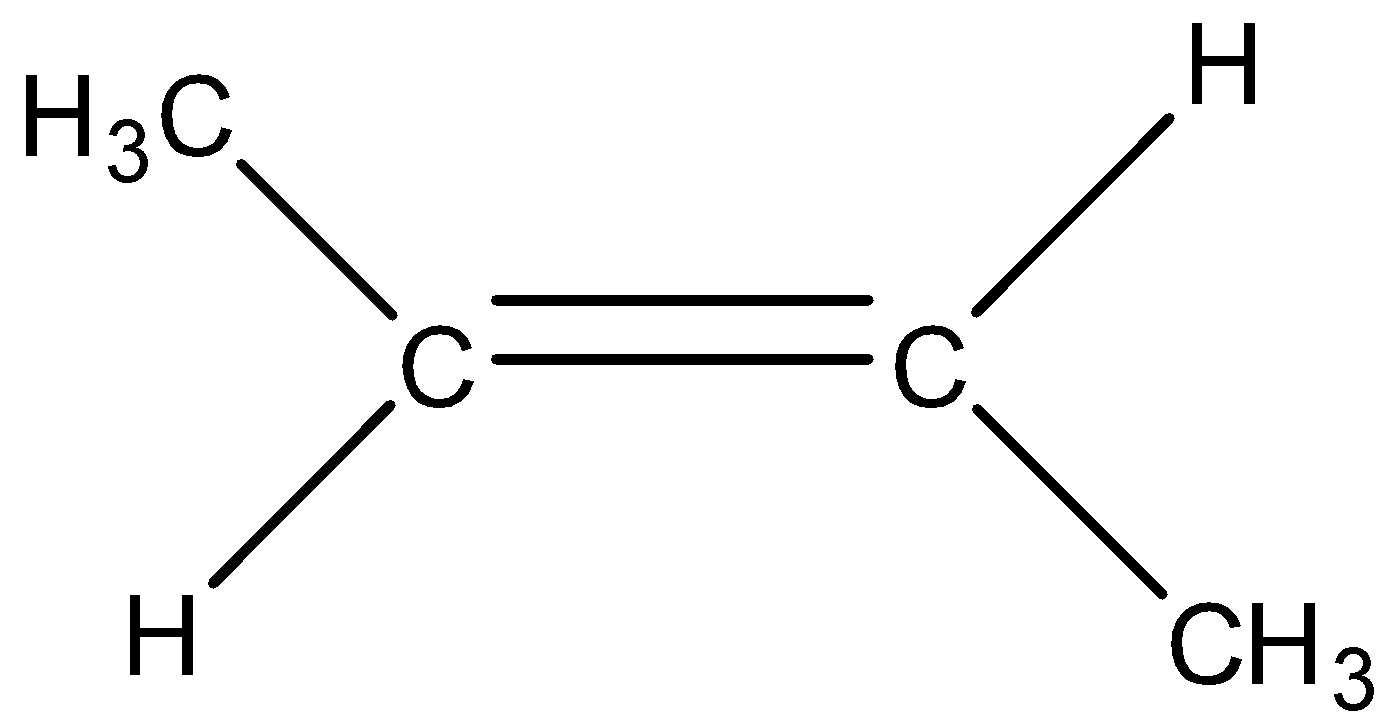
When the hydrogen atom is removed from the y position then there will be the formation of 1-butene having formula CH3−CH2−CH=CH2.
From the three products formed, 1-butene has the least stability, so it will have the highest potential energy. Trans-2-butene will have the highest stability so, it will have the lowest potential energy and cis-2-butene will have moderate potential energy. So, a will be 1-butene, b is cis-2-butene, and c is trans-2-butene.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (b).
Note:
It must be noted that the stability of the compound is inversely proportional to the potential energy of the compound. So, the higher the position of the compound in the graph, the less will be its stability.
