Question
Question: Endosmosis stops when the A. Solution becomes isotonic with respect to the surrounding solution ...
Endosmosis stops when the
A. Solution becomes isotonic with respect to the surrounding solution
B. Solution becomes hypertonic with respect to the surrounding solution
C. Wall becomes permeable with respect to the surrounding solution
D. Solution is kept in the dark with respect to the surrounding solution.
Solution
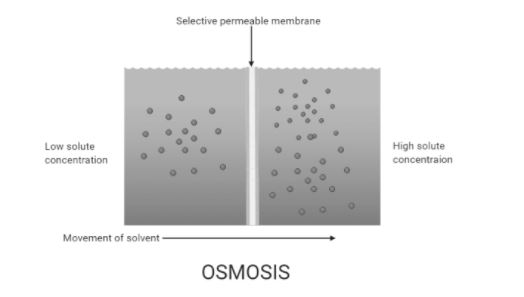
Osmosis involves movement of solvent molecules. Osmosis is of two types endosmosis and exosmosis. Endosmosis refers to the entry of solvent molecules inside the cell and exosmosis refers to the outward movement of solvent molecules from the cell.
Complete answer: The net movement that involves movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration is called osmosis. It tends to maintain an equal amount of the solute concentrations on the two sides inducing equilibrium on both sides. Most of the biological membranes are semipermeable and osmosis is a vital process in biological systems. Semipermeable membranes are not permeable to large and polar molecules which include ions, proteins, and polysaccharides. When a cell is allowed to obscure in water, the movement of water molecules takes place from a low solute concentration area to a high solute concentration area across the cell membrane. This is called endosmosis. For example, if a cell is submerged in saltwater, water molecules move out of the cell through the cell membrane as the solute concentration is higher outside the cell. This is called exosmosis. Whereas, if the cell is submerged in freshwater the water molecules will tend to move inside the cell by endosmosis. The movement of water molecules inside the cell stops when the solution becomes isotonic with respect to the surrounding solution. Isotonic refers to an equal concentration of both solute and solvent.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer.
Note: The term hypotonic refers to the solution with a low concentration of solutes and hypertonic refers to the high concentration of solutes in the solution. Water is the typical solvent in biological systems but osmosis can also occur through other liquids, gases, and supercritical liquids.
